Generalized Molluscum Contagiosum Successfully Treated with Interferon-Alpha in a Patient with Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides
- PMID: 31043940
- PMCID: PMC6477461
- DOI: 10.1159/000497349
Generalized Molluscum Contagiosum Successfully Treated with Interferon-Alpha in a Patient with Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides
Abstract
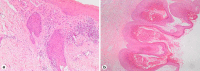
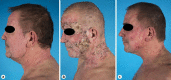
We present the case of a 50-year-old patient with folliculotropic mycosis fungoides (FMF) unresponsive to retinoids and the chemotherapeutic regimens CHOP, gemcitabine, and brentuximab-vedotin. During immunosuppressive therapy, the patient developed extensive progressive molluscum contagiosum. The mollusca did not respond to topical imiquimod but showed a swift complete response to interferon-alpha 2a (IFNa). Recently, the patient started with alemtuzumab as induction therapy for an allogenic stem cell transplantation and simultaneously continued IFNa therapy.
Keywords: Folliculotropic; Interferon alpha; Molluscum contagiosum; Mycosis fungoides.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Revisiting Imiquimod for Treatment of Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019 Dec;9(4):807-814. doi: 10.1007/s13555-019-00317-2. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2019. PMID: 31407190 Free PMC article.
-
Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides: Current Guidance and Experience from Clinical Practice.Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022 Sep 13;15:1899-1907. doi: 10.2147/CCID.S273063. eCollection 2022. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2022. PMID: 36124283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Syringotropic and folliculotropic mycosis fungoides with mycosis fungoides-associated vasculopathic ulcers.JAAD Case Rep. 2019 Feb 21;5(3):231-233. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2019.01.020. eCollection 2019 Mar. JAAD Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30834284 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Treatment of Early Folliculotropic Mycosis Fungoides with Special Focus on Psoralen plus Ultraviolet A.Acta Derm Venereol. 2018 Nov 5;98(10):951-955. doi: 10.2340/00015555-3013. Acta Derm Venereol. 2018. PMID: 30085321
-
Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome): part II. Prognosis, management, and future directions.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Feb;70(2):223.e1-17; quiz 240-2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.08.033. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 24438970 Review.
Cited by
-
The skin and soft tissue infections in hematological patients.Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2020 Apr;33(2):101-109. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000632. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32022740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Forbat E, Al-Niaimi F, Ali FR. Molluscum Contagiosum: Review and Update on Management. Pediatr Dermatol. 2017 Sep;34((5)):504–15. - PubMed
-
- DiBiagio JR, Pyle T, Green JJ. Reviewing the use of imiquimod for molluscum contagiosum. Dermatol Online J. 2018 Aug;24((6)):13030/qt3b4606qt. - PubMed
-
- Böhm M, Luger TA, Bonsmann G. Disseminated giant molluscum contagiosum in a patient with idiopathic CD4+ lymphocytopenia. Successful eradication with systemic interferon. Dermatology. 2008;217((3)):196–8. - PubMed
-
- Kilic SS, Kilicbay F. Interferon-alpha treatment of molluscum contagiosum in a patient with hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. Pediatrics. 2006 Jun;117((6)):e1253–5. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

