Transcriptomic analysis of human IL-7 receptor alpha low and high effector memory CD8+ T cells reveals an age-associated signature linked to influenza vaccine response in older adults
- PMID: 31044512
- PMCID: PMC6612637
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12960
Transcriptomic analysis of human IL-7 receptor alpha low and high effector memory CD8+ T cells reveals an age-associated signature linked to influenza vaccine response in older adults
Abstract
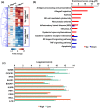
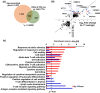
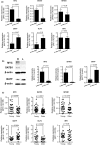
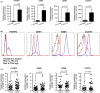
Here, we investigated the relationship of the age-associated expansion of IL-7 receptor alpha low (IL-7Rαlow ) effector memory (EM) CD8+ T cells with the global transcriptomic profile of peripheral blood cells in humans. We found 231 aging signature genes of IL-7Rαlow EM CD8+ T cells that corresponded to 15% of the age-associated genes (231/1,497) reported by a meta-analysis study on human peripheral whole blood from approximately 15,000 individuals, having high correlation with chronological age. These aging signature genes were the target genes of several transcription factors including MYC, SATB1, and BATF, which also belonged to the 231 genes, supporting the upstream regulatory role of these transcription factors in altering the gene expression profile of peripheral blood cells with aging. We validated the differential expression of these transcription factors between IL-7Rαlow and high EM CD8+ T cells as well as in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of young and older adults. Finally, we found a significant association with influenza vaccine responses in older adults, suggesting the possible biological significance of the aging signature genes of IL-7Rαlow EM CD8+ T cells. The results of our study support the relationship of the expansion of IL-7Rαlow EM CD8+ T cells with the age-associated changes in the gene expression profile of peripheral blood cells and its possible biological implications.
Keywords: IL-7 receptor alpha; age; gene expression; human; memory CD8+ T cells; vaccine response.
© 2019 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aging gene signature of memory CD8+ T cells is associated with neurocognitive functioning in Alzheimer's disease.Immun Ageing. 2023 Dec 2;20(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12979-023-00396-y. Immun Ageing. 2023. PMID: 38042785 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of IL-7 receptor alpha chain expression by CD8+ T cells and its signature in defining biomarkers in aging.Immun Ageing. 2022 Dec 21;19(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12979-022-00324-6. Immun Ageing. 2022. PMID: 36544153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Methylation Regulates the Differential Expression of CX3CR1 on Human IL-7Rαlow and IL-7Rαhigh Effector Memory CD8+ T Cells with Distinct Migratory Capacities to the Fractalkine.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 15;195(6):2861-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500877. Epub 2015 Aug 14. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26276874 Free PMC article.
-
IL-7Rαlow memory CD8+ T cells are significantly elevated in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012 Sep;51(9):1587-94. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kes100. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2012. PMID: 22661557 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and recall of CD8+ T-cell memory in a model of localized transient infection.Immunol Rev. 2006 Jun;211:133-45. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00386.x. Immunol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16824123 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunosenescence and Altered Vaccine Efficiency in Older Subjects: A Myth Difficult to Change.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Apr 13;10(4):607. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10040607. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Age-related factors that affect B cell responses to vaccination in mice and humans.Immunol Rev. 2020 Jul;296(1):142-154. doi: 10.1111/imr.12864. Epub 2020 Jun 2. Immunol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32484934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging gene signature of memory CD8+ T cells is associated with neurocognitive functioning in Alzheimer's disease.Immun Ageing. 2023 Dec 2;20(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12979-023-00396-y. Immun Ageing. 2023. PMID: 38042785 Free PMC article.
-
A novel unconventional T cell population enriched in Crohn's disease.Gut. 2022 Nov;71(11):2194-2204. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325373. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Gut. 2022. PMID: 35264446 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of IL-7 receptor alpha chain expression by CD8+ T cells and its signature in defining biomarkers in aging.Immun Ageing. 2022 Dec 21;19(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12979-022-00324-6. Immun Ageing. 2022. PMID: 36544153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buckler, A. J. , Vie, H. , Sonenshein, G. E. , & Miller, R. A. (1988). Defective T lymphocytes in old mice. Diminished production of mature c‐myc RNA after mitogen exposure not attributable to alterations in transcription or RNA stability. The Journal of Immunology, 140, 2442–2446. - PubMed
-
- Gamble, D. A. , Schwab, R. , Weksler, M. E. , & Szabo, P. (1990). Decreased steady state c‐myc mRNA in activated T cell cultures from old humans is caused by a smaller proportion of T cells that transcribe the c‐myc gene. The Journal of Immunology, 144, 3569–3573. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2R56AG0280691/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AG056728/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG021342/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG042489/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007107/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG021342/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG028069/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI126604/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI089992/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AG042489/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG056728/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG055362/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

