Digital pathology and artificial intelligence
- PMID: 31044723
- PMCID: PMC8711251
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30154-8
Digital pathology and artificial intelligence
Abstract
In modern clinical practice, digital pathology has a crucial role and is increasingly a technological requirement in the scientific laboratory environment. The advent of whole-slide imaging, availability of faster networks, and cheaper storage solutions has made it easier for pathologists to manage digital slide images and share them for clinical use. In parallel, unprecedented advances in machine learning have enabled the synergy of artificial intelligence and digital pathology, which offers image-based diagnosis possibilities that were once limited only to radiology and cardiology. Integration of digital slides into the pathology workflow, advanced algorithms, and computer-aided diagnostic techniques extend the frontiers of the pathologist's view beyond a microscopic slide and enable true utilisation and integration of knowledge that is beyond human limits and boundaries, and we believe there is clear potential for artificial intelligence breakthroughs in the pathology setting. In this Review, we discuss advancements in digital slide-based image diagnosis for cancer along with some challenges and opportunities for artificial intelligence in digital pathology.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
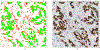


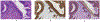
References
-
- Farahani N, Parwani AV, and Pantanowitz L, "Whole slide imaging in pathology: advantages, limitations, and emerging perspectives," Pathol Lab Med Int, vol. 7, pp. 23–33, 2015.
-
- Zarella MD, Bowman D, Aeffner F, Farahani N, Xthona A, Absar SF, Parwani A, Bui M, and Hartman DJ, "A Practical Guide to Whole Slide Imaging: A White Paper From the Digital Pathology Association," Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine, 2018. - PubMed
-
- Mirza M and Osindero S, "Conditional generative adversarial nets," arXiv preprint arXiv: 1411.1784, 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

