sEMG-angle estimation using feature engineering techniques for least square support vector machine
- PMID: 31045525
- PMCID: PMC6598017
- DOI: 10.3233/THC-199005
sEMG-angle estimation using feature engineering techniques for least square support vector machine
Abstract
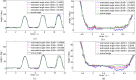
In the practical implementation of control of electromyography (sEMG) driven devices, algorithms should recognize the human's motion from sEMG with fast speed and high accuracy. This study proposes two feature engineering (FE) techniques, namely, feature-vector resampling and time-lag techniques, to improve the accuracy and speed of least square support vector machine (LSSVM) for wrist palmar angle estimation from sEMG feature. The root mean square error and correlation coefficients of LSSVM with FE are 9.50 ± 2.32 degree and 0.971 ± 0.018 respectively. The average training time and average execution time of LSSVM with FE in processing 12600 sEMG points are 0.016 s and 0.053 s respectively. To evaluate the proposed algorithm, its estimation results are compared with those of three other methods, namely, LSSVM, radial basis function (RBF) neural network, and RBF with FE. Experimental results verify that introduction of time-lag into feature vector can greatly improve the estimation accuracy of both RBF and LSSVM; meanwhile the application of feature-vector resampling technique can significantly increase the training and execution speed of RBF neural network and LSSVM. Among different algorithms applied in this study, LSSVM with FE techniques performed best in terms of training and execution speed, as well as estimation accuracy.
Keywords: Least square support vector machine; angle estimation; electromyograph; feature engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
None to report.
Figures









References
-
- Pradhan GN, Engineer N, Nadin M, et al. Integration of Motion Capture and EMG data for Classifying the Human Motions[C]// International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops, ICDE 2007, 15 20 April 2007, Istanbul, Turkey. DBLP, 2007; 56-63.
-
- Enoka RM, Neuromechanical basis of kinesiology, 2nd ed. Champaign: Human Kinetics, 1994, pp. 24-40.
-
- Mulas M, Folgheraiter M, Gini G. An EMG-controlled exoskeleton for hand rehabilitation, International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics IEEE. 2005; 371-374.
-
- Pons JL, et al., Virtual reality training and EMG control of the MANUS hand prosthesis, Robotica. 2005; 23(3): 311-317.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

