Genetic Predisposition Impacts Clinical Changes in a Lifestyle Coaching Program
- PMID: 31048771
- PMCID: PMC6497671
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-43058-0
Genetic Predisposition Impacts Clinical Changes in a Lifestyle Coaching Program
Abstract
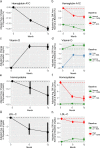
Both genetic and lifestyle factors contribute to an individual's disease risk, suggesting a multi-omic approach is essential for personalized prevention. Studies have examined the effectiveness of lifestyle coaching on clinical outcomes, however, little is known about the impact of genetic predisposition on the response to lifestyle coaching. Here we report on the results of a real-world observational study in 2531 participants enrolled in a commercial "Scientific Wellness" program, which combines multi-omic data with personalized, telephonic lifestyle coaching. Specifically, we examined: 1) the impact of this program on 55 clinical markers and 2) the effect of genetic predisposition on these clinical changes. We identified sustained improvements in clinical markers related to cardiometabolic risk, inflammation, nutrition, and anthropometrics. Notably, improvements in HbA1c were akin to those observed in landmark trials. Furthermore, genetic markers were associated with longitudinal changes in clinical markers. For example, individuals with genetic predisposition for higher LDL-C had a lesser decrease in LDL-C on average than those with genetic predisposition for average LDL-C. Overall, these results suggest that a program combining multi-omic data with lifestyle coaching produces clinically meaningful improvements, and that genetic predisposition impacts clinical responses to lifestyle change.
Conflict of interest statement
N.Z., M.C.P., A.T.M., J.C.L. are employees of Arivale and have stock options in the company. L.H. and N.D.P. are co-founders of Arivale and hold stock in the company. B.J.S. and G.S.O. also hold stock options in the company. N.D.P. is on the Arivale Board of Directors. L.H., G.S.O. and B.J.S. are members of Arivale’s Scientific Advisory Board.
Figures
References
-
- Appel LJ, et al. Effects of comprehensive lifestyle modification on blood pressure control: main results of the PREMIER clinical trial. JAMA. 2003;289:2083–2093. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

