Biodiversity of Bacteria Associated with Eight Pleurotus ostreatus (Fr.) P. Kumm. Strains from Poland, Japan and the USA
- PMID: 31050255
- PMCID: PMC7256699
- DOI: 10.21307/pjm-2019-009
Biodiversity of Bacteria Associated with Eight Pleurotus ostreatus (Fr.) P. Kumm. Strains from Poland, Japan and the USA
Abstract
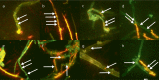
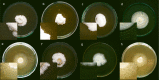
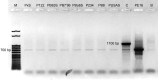
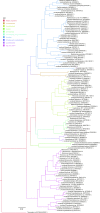
Few publications report the occurrence of bacteria associated with fungal cells. The presence of bacteria associated with one strain of Pleurotus ostreatus (Fr.) P. Kumm. was described in the literature. We describe the biodiversity of bacteria associated with eight oyster mushroom strains from Japan, Poland, and the USA. The presence of microorganisms associated with all tested P. ostreatus strains was confirmed using fluorescent microscopy. Among 307 sequences, 233 of clones representing 34 genera and 74 sequences were identified as Bacteria. Most of the bacteria associated with the strain PUSAS were related to E. coli and two clones were related to Cupriavidus genus. The biodiversity of clones isolated from fungal strains originating from Japan and Poland ranged from 15 to 32 different bacterial clones. The most often the bacteria related to genus Curvibacter, Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Cupriavidus, Pelomonas, and Propionibacterium were associated with the strains of fungi mentioned above. Laccase-like (LMCO) genes were identified in whole bacterial DNA isolated from the associated bacteria but β-glucosidase and β-xylanase genes were not detected.
Few publications report the occurrence of bacteria associated with fungal cells. The presence of bacteria associated with one strain of Pleurotus ostreatus (Fr.) P. Kumm. was described in the literature. We describe the biodiversity of bacteria associated with eight oyster mushroom strains from Japan, Poland, and the USA. The presence of microorganisms associated with all tested P. ostreatus strains was confirmed using fluorescent microscopy. Among 307 sequences, 233 of clones representing 34 genera and 74 sequences were identified as Bacteria. Most of the bacteria associated with the strain PUSAS were related to E. coli and two clones were related to Cupriavidus genus. The biodiversity of clones isolated from fungal strains originating from Japan and Poland ranged from 15 to 32 different bacterial clones. The most often the bacteria related to genus Curvibacter, Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Cupriavidus, Pelomonas, and Propionibacterium were associated with the strains of fungi mentioned above. Laccase-like (LMCO) genes were identified in whole bacterial DNA isolated from the associated bacteria but β-glucosidase and β-xylanase genes were not detected.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not report any financial or personal connections with other persons or organizations, which might negatively affect the contents of this publication and/or claim authorship rights to this publication.
Figures

References
-
- Bertaux J, Schmid M, Prevost-Boure NC, Churin JL, Hartmann A, Garbaye J, Frey-Klett P. In situ identification of intracellular bacteria related to Paenibacillus spp. in the mycelium of the ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor S238N. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69(7):4243–4248. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.7.4243-4248.2003 Medline - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bianciotto V, Lumini E, Lanfranco L, Minerdi D, Bonfante P, Perotto S. Detection and identification of bacterial endosymbionts in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi belonging to the family Gigasporaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2000;66(10):4503–4509. doi:10.1128/AEM.66.10.4503-4509.2000 Medline - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
