Circle the Wagons: Circular RNAs Control Innate Immunity
- PMID: 31051101
- PMCID: PMC7112311
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.04.020
Circle the Wagons: Circular RNAs Control Innate Immunity
Abstract
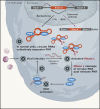
Circular RNAs are generated at low levels from many protein-coding genes. Liu et al. now reveal that many of these transcripts bind and inhibit the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-dependent kinase PKR. Upon viral infection, circular RNAs are globally degraded to release PKR, which becomes activated to aid in the immune response.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
J.E.W. is a consultant for VL50, Inc.
Figures
Comment on
-
Structure and Degradation of Circular RNAs Regulate PKR Activation in Innate Immunity.Cell. 2019 May 2;177(4):865-880.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.03.046. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31031002
References
-
- Khabar K.S., Siddiqui Y.M., al-Zoghaibi F., al-Haj L., Dhalla M., Zhou A., Dong B., Whitmore M., Paranjape J., Al-Ahdal M.N. RNase L mediates transient control of the interferon response through modulation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:20124–20132. - PubMed
-
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R.J., Safer B., Munemitsu S.M., Samuel C.E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986;45:195–200. - PubMed
-
- Liu C.-X., Li X., Nan F., Jiang S., Gao X., Guo S.-K., Xue W., Cui Y., Dong K., Ding H. Structure and degradation of circular RNAs regulate PKR activation in innate immunity. Cell. 2019;177:865–880. this issue. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

