Immobilisation of bacteria onto magnetic nanoparticles for the decolorisation and degradation of azo dyes
- PMID: 31051444
- PMCID: PMC8676242
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5026
Immobilisation of bacteria onto magnetic nanoparticles for the decolorisation and degradation of azo dyes
Abstract
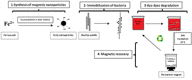
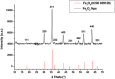
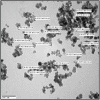
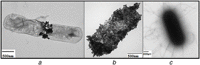
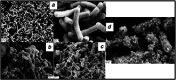
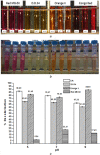
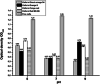
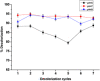
Azo dyes are widely used in industries and their release in the environment contributes to the pollution of effluents. The authors aim to develop a new eco-friendly water treatment method for the degradation of azo dyes based on in situ magnetic separation and immobilisation of bacterial cells. The immobilisation was achieved using superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and offers the possibility of reusing bacteria by magnetic separation for several degradation cycles. The iron-oxide nanoparticles were synthesised by reverse co-precipitation. The Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis were immobilised using iron-oxide nanoparticles by adsorption and then separated with an external magnetic field. Transmission electron microscopy observation showed that the particles' diameter was ∼20 nm with a narrow size distribution. Moreover, the iron-oxide nanoparticles were adsorbed onto the surface in order to coat the cells. B. subtilis has proved its ability to decolorise and degrade several azo dyes at different values of pH, with the highest decolorisation rate for Congo red. Furthermore, immobilised cells have a degradation activity similar to that of free cells. The system provided a degradation rate up to 80% and could be reused for seven batch cycles.
Figures






References
-
- Pandey A. Singh P. Iyengar L.: ‘Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes’, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 2007, 59, (2), pp. 73 –84
-
- Hao O.J. Kim H. Chiang P.‐C.: ‘Decolorization of wastewater’, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2000, 30, (4), pp. 449 –505
-
- Gupta V.: ‘Application of low‐cost adsorbents for dye removal–a review’, J. Environ. Manag., 2009, 90, (8), pp. 2313 –2342 - PubMed
-
- Saratale R.G. Saratale G.D. Chang et al.: ‘Bacterial decolorization and degradation of azo dyes: a review’, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2011, 42, (1), pp. 138 –157
-
- Vandevivere P.C. Bianchi R. Verstraete W.: ‘Treatment and reuse of wastewater from the textile wet‐processing industry: review of emerging technologies’, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 1998, 72, (4), pp. 289 –302
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

