Embossed Membranes with Vascular Patterns Guide Vascularization in a 3D Tissue Model
- PMID: 31052571
- PMCID: PMC6572394
- DOI: 10.3390/polym11050792
Embossed Membranes with Vascular Patterns Guide Vascularization in a 3D Tissue Model
Abstract
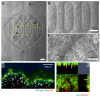
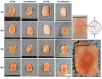
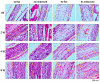
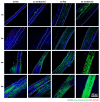
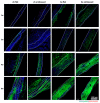
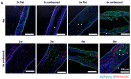
The vascularization of three-dimensional (3D) tissue constructs is necessary for transporting nutrients and oxygen to the component cells. In this study, a vacuum forming method was applied to emboss a vascular pattern on an electrospun membrane so that guided vascular structures could develop within the construct. Two- or six-layer constructs of electrospun membranes seeded with endothelial cells and pericytes were stacked and subcutaneously implanted into mice. Blood vessel formation in the implanted constructs with six alternating layers of flat membranes and membranes embossed with a blood vessel pattern was observed after two weeks of implantation. The formation of blood vessels was observed along the embossed blood vessel pattern in the structure of the embossed membrane laminated at four weeks and eight weeks. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and angiopoietin 1 (Ang-1) were highly expressed in the vascularized structures. Therefore, we demonstrated that a structure capable of producing a desired blood vessel shape with electrospun membranes embossed with a blood vessel pattern can be manufactured, and that a variety of structures can be manufactured using electrospun membranes in the tissue engineering era.
Keywords: 3D tissue; embossed membrane; guided vascularization; tissue-engineered vascularization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



References
-
- Novosel E.C., Kleinhans C., Kluger P.J. Vascularization is the key challenge in tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011;63:300–311. - PubMed
-
- Ramakrishna S., Fujihara K., Teo W.-E., Lim T.-C., Ma Z. An Introduction to Electrospinning and Nanofibers. World Scientific; Singapore: 2005. p. 396.
-
- Alamein M.A., Liu Q., Stephens S., Skabo S., Warnke F., Bourke R., Heiner P., Warnke P.H. Nanospiderwebs: Artificial 3d extracellular matrix from nanofibers by novel clinical grade electrospinning for stem cell delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013;2:702–717. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201200287. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sell S.A., Wolfe P.S., Garg K., McCool J.M., Rodriguez I.A., Bowlin G.L. The use of natural polymers in tissue engineering: A focus on electrospun extracellular matrix analogues. Polymers. 2010;2:522–553. doi: 10.3390/polym2040522. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

