PD-L1 (B7-H1) Competes with the RNA Exosome to Regulate the DNA Damage Response and Can Be Targeted to Sensitize to Radiation or Chemotherapy
- PMID: 31053471
- PMCID: PMC6737939
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.04.005
PD-L1 (B7-H1) Competes with the RNA Exosome to Regulate the DNA Damage Response and Can Be Targeted to Sensitize to Radiation or Chemotherapy
Abstract
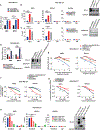
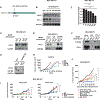
Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1, also called B7-H1) is an immune checkpoint protein that inhibits immune function through its binding of the programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) receptor. Clinically approved antibodies block extracellular PD-1 and PD-L1 binding, yet the role of intracellular PD-L1 in cancer remains poorly understood. Here, we discovered that intracellular PD-L1 acts as an RNA binding protein that regulates the mRNA stability of NBS1, BRCA1, and other DNA damage-related genes. Through competition with the RNA exosome, intracellular PD-L1 protects targeted RNAs from degradation, thereby increasing cellular resistance to DNA damage. RNA immunoprecipitation and RNA-seq experiments demonstrated that PD-L1 regulates RNA stability genome-wide. Furthermore, we developed a PD-L1 antibody, H1A, which abrogates the interaction of PD-L1 with CMTM6, thereby promoting PD-L1 degradation. Intracellular PD-L1 may be a potential therapeutic target to enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy and chemotherapy in cancer through the inhibition of DNA damage response and repair.
Keywords: CMTM6; DNA repair; PD-L1; PD-L1 destabilization; RNA binding; RNA exosome; anti-B7-H1 antibody; chemotherapy; immunotherapy; radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, Vicente D, Murakami S, Hui R, Yokoi T, Chiappori A, Lee KH, de Wit M, et al. (2017). Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 377, 1919–1929. - PubMed
-
- Chen DS, Irving BA, and Hodi FS (2012). Molecular pathways: next-generation immunotherapy--inhibiting programmed death-ligand 1 and programmed death-1. Clin Cancer Res 18, 6580–6587. - PubMed
-
- Chen N, Fang W, Zhan J, Hong S, Tang Y, Kang S, Zhang Y, He X, Zhou T, Qin T, et al. (2015). Upregulation of PD-L1 by EGFR Activation Mediates the Immune Escape in EGFR-Driven NSCLC: Implication for Optional Immune Targeted Therapy for NSCLC Patients with EGFR Mutation. J Thorac Oncol 10, 910–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

