Structural dissection reveals a general mechanistic principle for group II chitinase (ChtII) inhibition
- PMID: 31053640
- PMCID: PMC6579453
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007812
Structural dissection reveals a general mechanistic principle for group II chitinase (ChtII) inhibition
Abstract
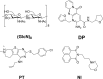
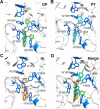
Small-molecule inhibitors of insect chitinases have potential applications for controlling insect pests. Insect group II chitinase (ChtII) is the most important chitinase in insects and functions throughout all developmental stages. However, the possibility of inhibiting ChtII by small molecules has not been explored yet. Here, we report the structural characteristics of four molecules that exhibited similar levels of inhibitory activity against OfChtII, a group II chitinase from the agricultural pest Asian corn borer Ostrinia furnacalis These inhibitors were chitooctaose ((GlcN)8), dipyrido-pyrimidine derivative (DP), piperidine-thienopyridine derivative (PT), and naphthalimide derivative (NI). The crystal structures of the OfChtII catalytic domain complexed with each of the four inhibitors at 1.4-2.0 Å resolutions suggested they all exhibit similar binding modes within the substrate-binding cleft; specifically, two hydrophobic groups of the inhibitor interact with +1/+2 tryptophan and a -1 hydrophobic pocket. The structure of the (GlcN)8 complex surprisingly revealed that the oligosaccharide chain of the inhibitor is orientated in the opposite direction to that previously observed in complexes with other chitinases. Injection of the inhibitors into 4th instar O. furnacalis larvae led to defects in development and pupation. The results of this study provide insights into a general mechanistic principle that confers inhibitory activity against ChtII, which could facilitate rational design of agrochemicals that target ecdysis of insect pests.
Keywords: Asian corn borer (Ostrinia furnacalis); X-ray crystallography; ecdysis; glycoside hydrolase; group II chitinase; inhibition mechanism; inhibitor; inhibitor design; insect; protein crystallization.
© 2019 Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

References
-
- Kramer K. J., and Koga D. (1986) Insect chitin: Physical state, synthesis, degradation and metabolic regulation. Insect Biochem. 16, 851–877 10.1016/0020-1790(86)90059-4 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

