Macrocyclic lactone anthelmintic-induced leukocyte binding to Dirofilaria immitis microfilariae: Influence of the drug resistance status of the parasite
- PMID: 31054498
- PMCID: PMC6500911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2019.04.004
Macrocyclic lactone anthelmintic-induced leukocyte binding to Dirofilaria immitis microfilariae: Influence of the drug resistance status of the parasite
Abstract
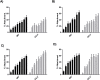
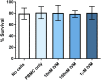
The macrocyclic lactone anthelmintics are the only class of drug currently used to prevent heartworm disease. Their extremely high potency in vivo is not mirrored by their activity against Dirofilaria immitis larvae in vitro, leading to suggestions that they may require host immune functions to kill the parasites. We have previously shown that ivermectin stimulates the binding of canine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) to D. immitis microfilariae (Mf). We have now extended these studies to moxidectin and examined the ability of both drugs to stimulate canine PBMC and PMN attachment to Mf from multiple strains of D. immitis, including two that are proven to be resistant to ivermectin in vivo. Both ivermectin and moxidectin significantly increased the percentage of drug-susceptible parasites with cells attached at very low concentrations (<10 nM), but much higher concentrations of ivermectin (>100 nM) were required to increase the percentage of the two resistant strains, Yazoo-2013 and Metairie-2014, with cells attached. Moxidectin increased the percentage of the two resistant strains with cells attached at lower concentrations (<10 nM) than did ivermectin. The attachment of the PBMCs and PMNs did not result in any parasite killing in vitro. These data support the biological relevance of the drug-stimulated attachment of canine leukocytes to D. immitis Mf and suggest that this phenomenon is related to the drug resistance status of the parasites.
Keywords: Dirofilaria immitis; Drug resistance; Ivermectin; Moxidectin; Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; Polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bourguinat C., Keller K., Blagburn B., Schenker R., Geary T.G., Prichard R.K. Correlation between loss of efficacy of macrocyclic lactone heartworm anthelmintics and P-glycoprotein genotype. Vet. Parasitol. 2011;176:374–381. - PubMed
-
- Bourguinat C., Lee A.C.Y., Lizundia R., Blagburn B.L., Liotta J.L., Kraus M.S., Keller K., Epe C., Letourneau L., Kleinman C.L., Paterson T., Gomez E.C., Montoya-Alonso J.A., Smith H., Bhan A., Peregrine A.S., Carmichael J., Drake J., Schenker R., Kaminsky R., Bowman D.D., Geary T.G., Prichard R.K. Macrocyclic lactone resistance in Dirofilaria immitis: failure of heartworm preventives and investigation of genetic markers for resistance. Vet. Parasitol. 2015;210:167–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

