Mitochondrial ClpP-Mediated Proteolysis Induces Selective Cancer Cell Lethality
- PMID: 31056398
- PMCID: PMC6620028
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.03.014
Mitochondrial ClpP-Mediated Proteolysis Induces Selective Cancer Cell Lethality
Abstract
The mitochondrial caseinolytic protease P (ClpP) plays a central role in mitochondrial protein quality control by degrading misfolded proteins. Using genetic and chemical approaches, we showed that hyperactivation of the protease selectively kills cancer cells, independently of p53 status, by selective degradation of its respiratory chain protein substrates and disrupts mitochondrial structure and function, while it does not affect non-malignant cells. We identified imipridones as potent activators of ClpP. Through biochemical studies and crystallography, we show that imipridones bind ClpP non-covalently and induce proteolysis by diverse structural changes. Imipridones are presently in clinical trials. Our findings suggest a general concept of inducing cancer cell lethality through activation of mitochondrial proteolysis.
Keywords: acute myeloid leukemia; cancer; imipridone; lymphoma; mitochondrial ClpP; mitochondrial proteolysis; oxidative phosphorylation; respiratory chain complex.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests:
M.S. is an employee and stockholder of Oncoceutics. M.A. serves on the scientific advisory board and is a stockholder of Oncoceutics. A.D.S has received consulting fees from Novartis, Jazz and Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, and research grants from Medivir and Takeda Pharmaceuticals, and holds stock in Abbvie, Adamas Pharmaceuticals, Insmed, Myovant Sciences, Theravance Biopharma. We have filed invention disclosure forms related to the use of ONC201 in AML with high ClpP expression.
Figures


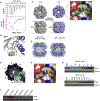
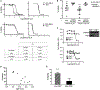
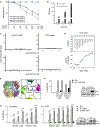


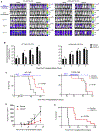
Comment in
-
The Direct Molecular Target for Imipridone ONC201 Is Finally Established.Cancer Cell. 2019 May 13;35(5):707-708. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2019.04.010. Cancer Cell. 2019. PMID: 31085171
References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkoczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, et al. (2010). PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta crystallographica Section D, Biological crystallography 66, 213–221. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Afonine PV, and Adams PD (2012). On the contribution of hydrogen atoms to X-ray scattering. Computational Crystallography Newsletter 3, 18–21.
-
- Allen JE, Krigsfeld G, Mayes PA, Patel L, Dicker DT, Patel AS, Dolloff NG, Messaris E, Scata KA, Wang W, et al. (2013). Dual inactivation of Akt and ERK by TIC10 signals Foxo3a nuclear translocation, TRAIL gene induction, and potent antitumor effects. Science translational medicine 5, 171ra117. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

