The protective effect and mechanism of rapamycin in the rat model of IgA nephropathy
- PMID: 31057050
- PMCID: PMC6507862
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1577257
The protective effect and mechanism of rapamycin in the rat model of IgA nephropathy
Abstract
Background: The pathogenesis of the development of IgA nephropathy has not been clear up to now. At present, some studies revealed that the mTOR pathway may participate in IgA nephropathy; however, the mechanism has not been systematically studied. In this study, we established an IgAN rat model to investigate the protective effects of rapamycin as a new type of immunosuppressant, as well as its therapeutic mechanisms.
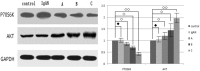
Methods: After the establishment of IgA nephropathy model, rats were treated with different concentrations of rapamycin, and the protective effect of different concentrations of rapamycin on renal function of the rats was observed. The deposition of IgA was observed by immunofluorescence. The kidney expression of Akt and p70S6k proteins in mTOR pathway was examined using the western blot assay after rapamycin treatment.
Results: Morphology and immunofluorescence confirmed that the rat model of IgA nephropathy was successfully established. In particular, the level of proteinuria decreased with the increase of the dose of rapamycin, as well as the deposition of IgA in glomeruli. Moreover, the western blot analysis indicated that the expression of p70S6K in the downstream of mTOR pathway decreased and the upstream protein AKT of the mTOR pathway was overexpressed in the rats model.
Conclusion: We found that rapamycin has protective effects in the IgA nephropathy rat model in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, the result of western blot assay suggested that rapamycin may display its therapeutic effects through interfering the AKT-mTOR-p70S6K signaling pathway.
Keywords: IgA nephropathy; animal model; mTOR pathway; rapamycin.
Figures


References
-
- Wyatt RJ, Julian BA. IgA nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2402–2414. - PubMed
-
- Wada J, Sugiyama H, Makino H. Pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Semin Nephrol. 2003;23:556–563. - PubMed
-
- Monteiro RC, Halbwachs-Mecarelli L, Roque-Barreira MC, et al. Charge and size of mesangial IgA in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1985; 28:666–671. - PubMed
-
- Segarra A. Progress in understanding the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy: new perspectives for the near future? Nefrologia Publicacion Oficial De La Sociedad Espanola Nefrologia. 2010;30:501. - PubMed
-
- Heitman J, Movva NR, Hall MN. Targets for cell cycle arrest by the immunosuppressant rapamycin in yeast. Science. 1991;253:905–909. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
