Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies a Range of Immunologically Related Functional Elaborations of Lymph Node Associated Lymphatic and Blood Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 31057546
- PMCID: PMC6478037
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00816
Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies a Range of Immunologically Related Functional Elaborations of Lymph Node Associated Lymphatic and Blood Endothelial Cells
Abstract
Lymphatic and blood vessels are formed by specialized lymphatic endothelial cells (LEC) and blood endothelial cells (BEC), respectively. These endothelial populations not only form peripheral tissue vessels, but also critical supporting structures in secondary lymphoid organs, particularly the lymph node (LN). Lymph node LEC (LN-LEC) also have been shown to have important immunological functions that are not observed in LEC from tissue lymphatics. LN-LEC can maintain peripheral tolerance through direct presentation of self-antigen via MHC-I, leading to CD8 T cell deletion; and through transfer of self-antigen to dendritic cells for presentation via MHC-II, resulting in CD4 T cell anergy. LN-LEC also can capture and archive foreign antigens, transferring them to dendritic cells for maintenance of memory CD8 T cells. The molecular basis for these functional elaborations in LN-LEC remain largely unexplored, and it is also unclear whether blood endothelial cells in LN (LN-BEC) might express similar enhanced immunologic functionality. Here, we used RNA-Seq to compare the transcriptomic profiles of freshly isolated murine LEC and BEC from LN with one another and with freshly isolated LEC from the periphery (diaphragm). We show that LN-LEC, LN-BEC, and diaphragm LEC (D-LEC) are transcriptionally distinct from one another, demonstrating both lineage and tissue-specific functional specializations. Surprisingly, tissue microenvironment differences in gene expression profiles were more numerous than those determined by endothelial cell lineage specification. In this regard, both LN-localized endothelial cell populations show a variety of functional elaborations that suggest how they may function as antigen presenting cells, and also point to as yet unexplored roles in both positive and negative regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses. The present work has defined in depth gene expression differences that point to functional specializations of endothelial cell populations in different anatomical locations, but especially the LN. Beyond the analyses provided here, these data are a resource for future work to uncover mechanisms of endothelial cell functionality.
Keywords: RNA-Seq; antigen presentation; chemokines; cytokines and receptors; endothelial cell; lymph node; lymphatic; scavenger receptors.
Figures

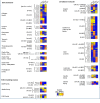
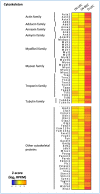
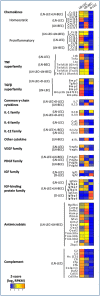
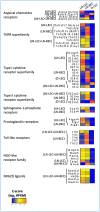
References
-
- Kriehuber E, Breiteneder-Geleff S, Groeger M, Soleiman A, Schoppmann SF, Stingl G, et al. Isolation and characterization of dermal lymphatic and blood endothelial cells reveal stable and functionally specialized cell lineages. J Exp Med. (2001) 194:797–808. 10.1084/jem.194.6.797 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lacorre DA, Baekkevold ES, Garrido I, Brandtzaeg P, Haraldsen G, Amalric F, et al. Plasticity of endothelial cells: rapid dedifferentiation of freshly isolated high endothelial venule endothelial cells outside the lymphoid tissue microenvironment. Blood. (2004) 103:4164–72. 10.1182/blood-2003-10-3537 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

