Phylogenetic Analyses and GAGA-Motif Binding Studies of BBR/BPC Proteins Lend to Clues in GAGA-Motif Recognition and a Regulatory Role in Brassinosteroid Signaling
- PMID: 31057577
- PMCID: PMC6477699
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00466
Phylogenetic Analyses and GAGA-Motif Binding Studies of BBR/BPC Proteins Lend to Clues in GAGA-Motif Recognition and a Regulatory Role in Brassinosteroid Signaling
Abstract
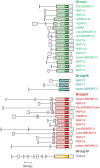
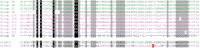
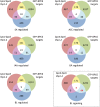
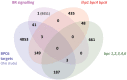
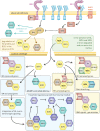
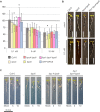
Plant GAGA-motif binding factors are encoded by the BARLEY B RECOMBINANT / BASIC PENTACYSTEINE (BBR/BPC) family, which fulfill indispensable functions in growth and development. BBR/BPC proteins control flower development, size of the stem cell niche and seed development through transcriptional regulation of homeotic transcription factor genes. They are responsible for the context dependent recruitment of Polycomb repressive complexes (PRC) or other repressive proteins to GAGA-motifs, which are contained in Polycomb repressive DNA-elements (PREs). Hallmark of the protein family is the highly conserved BPC domain, which is required for DNA binding. Here we study the evolution and diversification of the BBR/BPC family and its DNA-binding domain. Our analyses supports a further division of the family into four main groups (I-IV) and several subgroups, to resolve a strict monophyletic descent of the BPC domain. We prove a polyphyletic origin for group III proteins, which evolved from group I and II members through extensive loss of domains in the N-terminus. Conserved motif searches lend to the identification of a WAR/KHGTN consensus and a TIR/K motif at the very C-terminus of the BPC-domain. We could show by DPI-ELISA that this signature is required for DNA-binding in AtBPC1. Additional binding studies with AtBPC1, AtBPC6 and mutated oligonucleotides consolidated the binding to GAGA tetramers. To validate these findings, we used previously published ChIP-seq data from GFP-BPC6. We uncovered that many genes of the brassinosteroid signaling pathway are targeted by AtBPC6. Consistently, bpc6, bpc4 bpc6, and lhp1 bpc4 bpc4 mutants display brassinosteroid-dependent root growth phenotypes. Both, a function in brassinosteroid signaling and our phylogenetic data supports a link between BBR/BPC diversification in the land plant lineage and the complexity of flower and seed plant evolution.
Keywords: BBR/BPC proteins; GAGA-binding domain; GAGA-factors (GAF); PRE; Polycomb repressive complexes; basic Pentacysteine transcription factors.
Figures






References
-
- Berendzen K. W., Stuber K., Harter K., Wanke D. (2006). Cis-motifs upstream of the transcription and translation initiation sites are effectively revealed by their positional disequilibrium in eukaryote genomes using frequency distribution curves. BMC Bioinformatics 7:522. 10.1186/1471-2105-7-522 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

