High-fidelity replication of thermoplastic microneedles with open microfluidic channels
- PMID: 31057872
- PMCID: PMC6445010
- DOI: 10.1038/micronano.2017.34
High-fidelity replication of thermoplastic microneedles with open microfluidic channels
Abstract
Development of microneedles for unskilled and painless collection of blood or drug delivery addresses the quality of healthcare through early intervention at point-of-care. Microneedles with submicron to millimeter features have been fabricated from materials such as metals, silicon, and polymers by subtractive machining or etching. However, to date, large-scale manufacture of hollow microneedles has been limited by the cost and complexity of microfabrication techniques. This paper reports a novel manufacturing method that may overcome the complexity of hollow microneedle fabrication. Prototype microneedles with open microfluidic channels are fabricated by laser stereolithography. Thermoplastic replicas are manufactured from these templates by soft-embossing with high fidelity at submicron resolution. The manufacturing advantages are (a) direct printing from computer-aided design (CAD) drawing without the constraints imposed by subtractive machining or etching processes, (b) high-fidelity replication of prototype geometries with multiple reuses of elastomeric molds, (c) shorter manufacturing time compared to three-dimensional stereolithography, and (d) integration of microneedles with open-channel microfluidics. Future work will address development of open-channel microfluidics for drug delivery, fluid sampling and analysis.
Keywords: drug delivery; laser lithography; microneedles; point-of-care diagnostics; soft embossing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

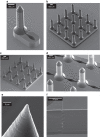

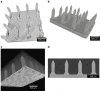
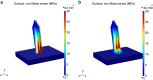



References
-
- Yung KL, Xu X, Kang C et al. Sharp tipped plastic hollow microneedle array by microinjection moulding. Journal of Micromechanics and Microengineering 2012; 22: 015016.
-
- Izumi H, Aoyagi S. Novel fabrication method for long silicon microneedles with three-dimensional sharp tips and complicated shank shapes by isotropic dry etching. IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering 2007; 2: 328–334.
-
- Yun S-S, An J-Y, Moon S-H et al. In-plane microneedle chip fabricated by crystalline wet etching of (110) silicon wafer. TRANSDUCERS 2009—International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference 2009; 21–25 June 2009; Denver, CO, USA; 2009: 204–207.
-
- Khumpuang S, Ruther P, Paul O. Micromolding methods for hollow microneedle arrays using megasonically enhanced casting. TRANSDUCERS 2009—International Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference 2009; 21–25 June 2009; Denver, CO, USA; 2009: 220–223.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
