Long-term Audiometric Outcomes in Unilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss without Recurrence
- PMID: 31058596
- PMCID: PMC6483438
- DOI: 10.5152/iao.2019.6670
Long-term Audiometric Outcomes in Unilateral Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss without Recurrence
Abstract
Objectives: The recurrence rate of sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL) varies from 0.8% to 40%. However, to the best of our knowledge, no data on long-term hearing variations are present in the literature. The aim of this observational study was to analyze long-term variations of the hearing threshold in unilateral SSNHL without recurrence.
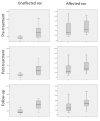
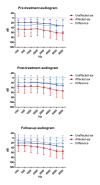
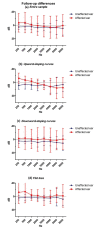
Materials and methods: A total of 50 patients affected by unilateral SSNHL were evaluated. Patients underwent a treatment consisting of intravenous corticosteroids. Clinical and audiometric features were recorded. Patients underwent pure tone audiometry at a mean follow-up of 5.26±2.28 years. Differences between the affected and unaffected ear were analyzed.
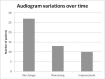
Results: Comparing the post-treatment and follow-up audiograms, there was a worsening of hearing in the unaffected ear. On the contrary, no significant difference over time was found for the affected ear. 54% of patients showed no changes over time, 26% showed worsening, and 20% showed an improvement in hearing. The variation correlated with alcohol consumption and the presence of vasculopathies. An average improvement of hearing over time was observed at low frequencies.
Conclusion: The time evolution in SSNHL is not predictable on the basis of the clinical and audiometric data. The majority the patients shows no changes in hearing loss in the affected ear. Patients who consume alcohol or have vasculopathies also have a higher risk of worsening of hearing. Further prospective studies are mandatory to better assess variations over time and their relationship with the effect of aging on hearing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures