Polyphenols in the treatment of autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 31059841
- PMCID: PMC6588481
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2019.05.001
Polyphenols in the treatment of autoimmune diseases
Abstract
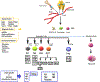
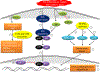
In addition to protecting body from infections and diseases, the immune system produces auto-antibodies that can cause complex autoimmune disorders, such as Type I diabetes, primary biliary cirrhosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis, to name a few. In such cases, the immune system fails to recognize between foreign agents and its own body cells. Different factors, such as genetic factors (CD25, STAT4), epigenetic factors (DNA methylation, histone modifications) and environmental factors (xenobiotics, drugs, hormones) trigger autoimmunity. Glucocorticoids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), immunosuppressive and biological agents are currently used to manage autoimmune diseases of different origins. However, complete cure remains elusive. Many dietary and natural products including polyphenols have been widely studied as possible alternative treatment strategies for the management of autoimmune disorders. Polyphenols possess a wide-range of pharmacological and therapeutic properties, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. As immunomodulatory agents, polyphenols are emerging pharmaceutical tools for management of various autoimmune disorders including vitiligo, ulcerative colitis and multiple sclerosis (MS). Polyphenols activate intracellular pathways such as arachidonic acid dependent pathway, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathway, mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) pathway, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/Akt) signaling pathway and epigenetic modulation, which regulate the host's immune response. This timely review discusses putative points of action of polyphenols in autoimmune diseases, characterizing their efficacy and safety as therapeutic agents in managing autoimmune disorders.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Epigenetic modulation; MAPKs; NF-κB; PI3K/Akt; Polyphenols.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Rengasamy KRR, Khan H, Gowrishankar S, Lagoa RJL, Mahomoodally FM, Khan Z, et al. The role of flavonoids in autoimmune diseases: Therapeutic updates. Pharmacol Ther 2019;194:107–31. - PubMed
-
- Wang L, Wang FS, Gershwin ME. Human autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive update. J Internal Med 2015;278:369–95. - PubMed
-
- Konforte D, Diamandis EP, van Venrooij WJ, Lories R, Ward MM. Autoimmune diseases: early diagnosis and new treatment strategies. Clin Chem 2012;58:1510–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

