Targeting Human Parainfluenza Virus Type-1 Haemagglutinin-Neuraminidase with Mechanism-Based Inhibitors
- PMID: 31060278
- PMCID: PMC6563277
- DOI: 10.3390/v11050417
Targeting Human Parainfluenza Virus Type-1 Haemagglutinin-Neuraminidase with Mechanism-Based Inhibitors
Abstract
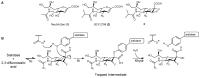
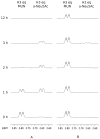
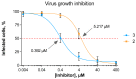
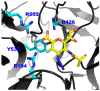
Human parainfluenza virus (hPIV) infections are a major cause of respiratory tract illnesses in children, with currently no available vaccine or drug treatment. The surface glycoprotein haemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) of hPIV has a central role in the viral life cycle, including neuraminic acid-recognising receptor binding activity (early stage) and receptor-destroying activity (late stage), which makes it an ideal target for antiviral drug disovery. In this study, we showed that targeting the catalytic mechanism of hPIV-1 HN by a 2α,3β-difluoro derivative of the known hPIV-1 inhibitor, BCX 2798, produced more potent inhibition of the neuraminidase function which is reflected by a stronger inhibition of viral replication. The difluorosialic acid-based inhibitor efficiently blocked the neuraminidase activity of HN for a prolonged period of time relative to its unsaturated neuraminic acid (Neu2en) analogue, BCX 2798 and produced a more efficient inhibition of the HN neuraminidase activity as well as in vitro viral replication. This prolonged inhibition of the hPIV-1 HN protein suggests covalent binding of the inhibitor to a key catalytic amino acid, making this compound a new lead for a novel class of more potent hPIV-1 mechanism-based inhibitors.
Keywords: difluorosialic acid; glycohydrolase; haemagglutinin; inhibitor; neuraminidase; parainfluenza; sialidase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Karron R.A., Collins P.L. Fields Virology: Sixth Edition. Volume 1 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2013. Parainfluenza viruses.
-
- Abedi G.R., Prill M.M., Langley G.E., Wikswo M.E., Weinberg G.A., Curns A.T., Schneider E. Estimates of Parainfluenza Virus-Associated Hospitalizations and Cost Among Children Aged Less Than 5 Years in the United States, 1998–2010. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2016;5:7–13. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piu047. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

