Rapid Covalent-Probe Discovery by Electrophile-Fragment Screening
- PMID: 31060360
- PMCID: PMC6556873
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.9b02822
Rapid Covalent-Probe Discovery by Electrophile-Fragment Screening
Abstract
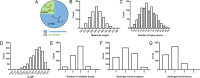
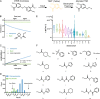
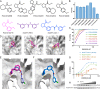
Covalent probes can display unmatched potency, selectivity, and duration of action; however, their discovery is challenging. In principle, fragments that can irreversibly bind their target can overcome the low affinity that limits reversible fragment screening, but such electrophilic fragments were considered nonselective and were rarely screened. We hypothesized that mild electrophiles might overcome the selectivity challenge and constructed a library of 993 mildly electrophilic fragments. We characterized this library by a new high-throughput thiol-reactivity assay and screened them against 10 cysteine-containing proteins. Highly reactive and promiscuous fragments were rare and could be easily eliminated. In contrast, we found hits for most targets. Combining our approach with high-throughput crystallography allowed rapid progression to potent and selective probes for two enzymes, the deubiquitinase OTUB2 and the pyrophosphatase NUDT7. No inhibitors were previously known for either. This study highlights the potential of electrophile-fragment screening as a practical and efficient tool for covalent-ligand discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


References
-
- Noe M. C.; Gilbert A. M.. Targeted Covalent Enzyme Inhibitors. In Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry; Elsevier: 2012; Vol. 47, pp 413–439.
-
- Bradshaw J. M.; McFarland J. M.; Paavilainen V. O.; Bisconte A.; Tam D.; Phan V. T.; Romanov S.; Finkle D.; Shu J.; Patel V.; Ton T.; Li X.; Loughhead D. G.; Nunn P. A.; Karr D. E.; Gerritsen M. E.; Funk J. O.; Owens T. D.; Verner E.; Brameld K. A.; Hill R. J.; Goldstein D. M.; Taunton J. Prolonged and Tunable Residence Time Using Reversible Covalent Kinase Inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11 (7), 525–531. 10.1038/nchembio.1817. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

