Sexually transmitted infections in young people and factors associated with HIV coinfection: an observational study in a large city
- PMID: 31061051
- PMCID: PMC6502227
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027245
Sexually transmitted infections in young people and factors associated with HIV coinfection: an observational study in a large city
Abstract
Objectives: Young people are a critical target group for sexually transmitted infections (STI) surveillance due to their particular behavioural and social related vulnerability. The aim of this study was to describe the epidemiological characteristics and trends in the incidence of gonorrhoea, syphilis, HIV and venereal lymphogranuloma (LGV) among 15-24-year-olds in Barcelona, and to determine factors associated with HIV coinfection.
Design: We performed a population-based incidence study covering the 2007-2015 period.
Participants: All new cases of STI-HIV, gonorrhoea, infectious syphilis and LGV-notified to the epidemiological surveillance system in Barcelona between 2007 and 2015. 1218 cases were studied: 84.6% were men, 19.3% were 15-19 years old and 50.6% were born in Spain. Among men, 73.7% were men who have sex with men (MSM); among women, 85.6% were women that have sex with men.
Primary and secondary outcomes: Incidence of HIV, gonorrhoea, infectious syphilis and LGV. HIV coinfection.
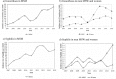
Results: There was an increase in the incidence of gonorrhoea, from 1.9 cases per 10 000 people in 2007 to 7.6/10 000 in 2015 (p<0.01), in MSM from 27.1 to 228.8/10 000 (p<0.01). The incidence of syphilis increased from 0.4/10 000 in 2007 to 3.1/10 000 in 2015 (significant in men only, p<0.01), in MSM from 18.1 to 116.9/10 000 (p<0.01). The incidence of HIV showed a non-significant increase in men (p=0.27), and that of LGV remained stable (p=0.59). Factors associated with increased risk of HIV coinfection included being MSM (adjusted OR[ORa]=14.14, 95% CI 3.34 to 59.91) and having >10 sexual partners (ORa=4.11, 95% CI 1.53 to 11.01) or STI diagnosis during the previous 12 months (ORa=2.06; 95% CI 1.13 to 3.77).
Conclusions: The incidence of gonorrhoea and syphilis among 15-24-year-olds increased, while HIV infection remained stable but with a high incidence among MSM. Being MSM, having sex with multiple partners and having a diagnosis of an STI in the previous 12 months were factors associated with HIV coinfection.
Keywords: Hiv coinfection; adolescents; incidence study; sexually transmitted infections; trends; young people.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs). http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs110/en/ (accessed 26 Feb 2018). - PubMed
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Sexually transmitted infections in Europe 2013. Stockholm: ECDC, 2015. https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/media/en/publications/Publicat....
-
- Área de vigilancia del VIH y conductas de riesgo. Vigilancia epidemiológica de las infecciones de transmisión sexual 1995-2015. Madrid: Centro Nacional de Epidemiología/Subdirección General de Promoción de la Salud y Epidemiología - Plan Nacional sobre el Sida, 2017. https://www.msssi.gob.es/en/ciudadanos/enfLesiones/enfTransmisibles/sida... (accessed 8 Aug 2017).
-
- Área de Vigilancia de VIH y Comportamientos de Riesgo. Vigilancia Epidemiológica del VIH y sida en España: Sistema de Información sobre Nuevos Diagnósticos de VIH y Registro Nacional de Casos de Sida. Madrid: S.G. de Promoción de la Salud y Epidemiología / Centro Nacional de Epidemiología - Plan Nacional sobre el Sida - ISCIII, 2016: https://www.msssi.gob.es/ciudadanos/enfLesiones/enfTransmisibles/sida/vi... (accessed 22 May 2017).
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. HIV and AIDS. In: ECDC. Annual epidemiological report for 2015. Stockholm: ECDC, 2017. https://ecdc.europa.eu/sites/portal/files/documents/AER_for_2015-HIV-AID... (accessed 26 Feb 2018).
