Identification of a Carbapenemase-Producing Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolate in the United States
- PMID: 31061159
- PMCID: PMC6591612
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00519-19
Identification of a Carbapenemase-Producing Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolate in the United States
Abstract
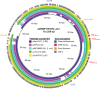
We report on a carbapenemase-producing hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (CP-hvKP) isolate collected from a U.S. patient at an outpatient clinic. The isolate was identified as K. pneumoniae serotype K1 sequence type 23 and included both a hypervirulence (with rmpA, rmpA2 iroBCDN, peg-344, and iucABCD-iutA genes) and a carbapenemase-encoding (blaKPC-2) plasmid. The emergence of CP-hvKP underscores the importance of clinical awareness of this pathotype and the need for continued monitoring of CP-hvKP in the United States.
Keywords: Klebsiella; hypervirulence; plasmid-mediated resistance.
This is a work of the U.S. Government and is not subject to copyright protection in the United States. Foreign copyrights may apply.
Figures

References
-
- Yigit H, Queenan AM, Anderson GJ, Domenech-Sanchez A, Biddle JW, Steward CD, Alberti S, Bush K, Tenover FC. 2001. Novel carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase, KPC-1, from a carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:1151–1161. doi:10.1128/AAC.45.4.1151-1161.2001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yigit H, Queenan AM, Rasheed JK, Biddle JW, Domenech-Sanchez A, Alberti S, Bush K, Tenover FC. 2003. Carbapenem-resistant strain of Klebsiella oxytoca harboring carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase KPC-2. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:3881–3889. doi:10.1128/AAC.47.12.3881-3889.2003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

