A Fully-Flexible Solution-Processed Autonomous Glucose Indicator
- PMID: 31061428
- PMCID: PMC6502809
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-43425-x
A Fully-Flexible Solution-Processed Autonomous Glucose Indicator
Abstract
We present the first demonstration of a fully-flexible, self-powered glucose indicator system that synergizes two flexible electronic technologies: a flexible self-powering unit in the form of a biofuel cell, with a flexible electronic device - a circuit-board decal fabricated with biocompatible microbial nanocellulose. Our proof-of-concept device, comprising an enzymatic glucose fuel cell, glucose sensor and a LED indicator, does not require additional electronic equipment for detection or verification; and the entire structure collapses into a microns-thin, self-adhering, single-centimeter-square decal, weighing less than 40 mg. The flexible glucose indicator system continuously operates a light emitting diode (LED) through a capacitive charge/discharge cycle, which is directly correlated to the glucose concentration. Our indicator was shown to operate at high sensitivity within a linear glucose concentration range of 1 mM-45 mM glucose continuously, achieving a 1.8 VDC output from a flexible indicator system that deliver sufficient power to drive an LED circuit. Importantly, the results presented provide a basis upon which further development of indicator systems with biocompatible diffusing polymers to act as buffering diffusion barriers, thereby allowing them to be potentially useful for low-cost, direct-line-of-sight applications in medicine, husbandry, agriculture, and the food and beverage industries.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



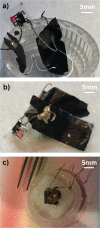
References
-
- Atzori L, Iera A, Morabito G. The internet of things: A survey. Computer networks. 2010;54:2787–2805. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2010.05.010. - DOI
-
- Gubbi J, Buyya R, Marusic S, Palaniswami M. Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions. Future generation computer systems. 2013;29:1645–1660. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2013.01.010. - DOI
-
- Hsu CL, Lin JCC. An empirical examination of consumer adoption of Internet of Things services: Network externalities and concern for information privacy perspectives. Computers in Human Behavior. 2016;62:516–527. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.04.023. - DOI
-
- Zhan Y, Mei Y, Zheng L. Materials capability and device performance in flexible electronics for the Internet of Things. Journal of Materials Chemistry C. 2014;2:1220–1232. doi: 10.1039/C3TC31765J. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

