Response to Therapy, Treatment Intolerance and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Cessation Eligibility in a Real-World Cohort of Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Patients
- PMID: 31061559
- PMCID: PMC6500416
Response to Therapy, Treatment Intolerance and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Cessation Eligibility in a Real-World Cohort of Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Patients
Abstract
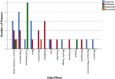
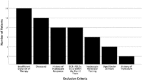
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy has revolutionised chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) management, it is however associated with significant side effects and economic burden. Recent studies have demonstrated that treatment free remission is possible in certain patients. The aim of this study was to characterise a real-world population in terms of response to therapy, treatment intolerance and potential eligibility for stopping treatment. Included were 105 CML patients diagnosed in Northern Ireland from March 2009-February 2018. Response to treatment was defined as per the 2009 and 2013 European Leukaemia Net guidelines. Potential for treatment cessation was assessed as per the 2017 UK Interim Expert Opinion on Discontinuing Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment in Clinical Practice for Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia. Our cytogenetic data cohort had a 12-month complete cytogenetic response rate of 66% and the molecular data cohort had a 12-month major molecular response rate of 38%. Of those commenced on 2nd line TKI therapy 81% achieved an optimal response at 12 months. Twenty-two patients developed intolerance and required a change in TKI therapy. The commonest side effects were gastro-intestinal upset (18%), transaminitis (16%) and fluid retention (16%). In our cohort, 20% were considered eligible to stop TKI therapy. The commonest reason for ineligibility was insufficient duration of therapy (25%). We observed that 1st and 2nd line TKI therapy are effective but problems with failure and intolerance persist. Additionally, this study identifies a cohort of patients who may attempt TKI cessation using the UK Interim Expert Opinion report on TKI therapy discontinuation.
Keywords: CML; TKI; intolerance; real-world; treatment cessation.
Conflict of interest statement
Provenance: externally peer reviewed
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67((1)):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Jabbour E, Kantarjian H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2016 update on diagnosis, therapy, and monitoring. Am J Hematol. 2016;91((2)):252–65. - PubMed
-
- Ren R. Mechanisms of BCR–ABL in the pathogenesis of chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5((3)):172–6. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F, et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2003;348((11)):994–1004. - PubMed
-
- Deininger M, O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Goldman JM, Hochhaus A, Hughes TP, et al. International Randomized Study of Interferon Vs STI571 (IRIS) 8-Year Follow up: sustained survival and low risk for progression or events in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) treated with Imatinib. Blood. 2009;114((22)):1126.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
