Multidisciplinary approach with predictable esthetics: A case report
- PMID: 31061609
- PMCID: PMC6488715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2019.01.007
Multidisciplinary approach with predictable esthetics: A case report
Abstract
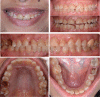
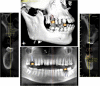
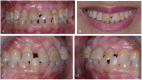
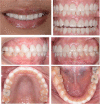
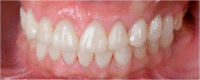
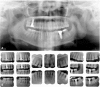
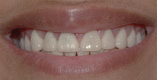
This case report explains an effective multidisciplinary approach used to improve the function, biology, and esthetic of a patient presented with an excessive gingival display, a spacing between anterior teeth, small size anterior teeth in maxilla and mandible. Also, unrestorable molars were noted with multiple carious lesions. The treatment combined crown lengthening, prosthetic dentistry using lithium disilicate crowns and minimally invasive implants placement approach.
Keywords: Crown lengthening; Dental implant; Esthetic dentistry; Excessive gingival display; High smile line; Multidisciplinary dentistry.
Figures




References
-
- Alam Mohammad, Sabir Mohammad. DENTAL SCIENCE review article multidisciplinary approach in modern dentistry: an innovation in advance dental care. EC Dental Sci. J. 2015;1
-
- Assaf Mohammad. Esthetic crown lengthening for upper anterior teeth: indications and surgical techniques. Int. J. Prevent. Clin. Dental Res. 2014;1(2):49–53.
-
- Becker William, Goldstein Moshe, Becker Burton E. Minimally invasive flapless implant surgery: a prospective multicenter study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2005:21–27. - PubMed
-
- Korkut B. Simulating natural dental outlook in esthetic dentistry: a case report. Int. J. Med. Sci. Clin. Invent. 2016;3(9) https://valleyinternational.net/index.php/ijmsci/article/view/547
-
- Kurian Bijo, Dv Swapna, Khatib Mohd Sibghatullah. Anterior aesthetic rehabilitation: a case report. Int. J. Appl. Dental Sci. 2018;4(1):6–8.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

