Effect of tea catechins with caffeine on energy expenditure in middle-aged men and women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial
- PMID: 31062079
- PMCID: PMC7098939
- DOI: 10.1007/s00394-019-01976-9
Effect of tea catechins with caffeine on energy expenditure in middle-aged men and women: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial
Abstract
Purpose: It has been reported that tea catechins increase energy metabolism, but their effect on resting metabolic rate (RMR) remains under debate. This study aimed to examine the effect of repeated intake of tea catechins on energy metabolism in the resting state in middle-aged men and women.
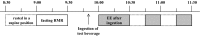
Methods: A total of 30 middle-aged men and women [13 women; age (mean ± SD) 52 ± 4 years; BMI 21.9 ± 2.2 kg/m2] were recruited. A randomized, double-blind, crossover study was conducted using a tea catechin-enriched beverage (611 mg catechins, 88 mg caffeine) and a placebo beverage (0 mg catechins, 81 mg caffeine) as test beverages. After 2 weeks of continuous test beverage intake, fasting RMR and energy expenditure (EE) after the ingestion of test beverage were measured. Measurements of forehead temperature (proxy for core temperature) and skin temperature were also obtained simultaneously.
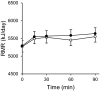
Results: Among participants who underwent measurements, 26 (10 women; mean age 52 ± 4 years; mean BMI 22.1 ± 2.1 kg/m2) were analyzed. The EE increased significantly after ingestion of the tea catechin beverage compared with the placebo beverage (placebo treatment: 5502 ± 757 kJ/day; catechin treatment: 5598 ± 800 kJ/day; P = 0.041). No between-treatment differences in fasting RMR or the respiratory quotient were detected. In addition, the forehead and skin temperature did not differ significantly between the placebo and catechin treatments.
Conclusion: This study revealed that continuous intake of tea catechins with caffeine for 2 weeks significantly increased EE after ingestion of the tea catechin but not fasting RMR in middle-aged men and women.
Clinical trial registry number and website: This trial was registered at www.umin.ac.jp/ctr/ as UMIN000025810 and UMIN000025811.
Keywords: Body temperature; Energy expenditure; Middle-aged men and women; Resting metabolic rate; Tea catechins.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by Kao Corporation. S. Katada, A. Yanagimoto, Y. Matsui, M. Hibi, N. Osaki, and Y. Katsuragi are employees of the Kao Corporation. S. Kobayashi has no personal or financial conflicts of interest. The sponsor had no control over the interpretation, writing, or publication of this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

