Neointimal hyperplasia of ultra-thin stents with microcrystalline sirolimus or durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents: 6- and 24-month results of the DESSOLVE III OCT study
- PMID: 31062697
- PMCID: PMC9724984
- DOI: 10.4244/EIJ-D-18-01201
Neointimal hyperplasia of ultra-thin stents with microcrystalline sirolimus or durable polymer everolimus-eluting stents: 6- and 24-month results of the DESSOLVE III OCT study
Abstract
Aims: The DESSOLVE III OCT substudy aimed to compare serially neointimal hyperplasia volume obstruction (%VO) between the thin-strut MiStent with early polymer elimination and nine-month sustained drug release from microcrystalline sirolimus and the durable polymer-coated everolimus-eluting XIENCE stent at six and 24 months after implantation.
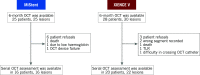
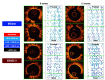
Methods and results: The efficacy endpoint was %VO, calculated as abluminal neointimal volume/stent volume. Thirty-six patients (MiStent 16 patients, 16 lesions; XIENCE 20 patients, 22 lesions) underwent serial OCT evaluation at both six and 24 months. At six months, mean abluminal %VO was significantly lower in the MiStent group than in the XIENCE group (14.54±3.70% vs 19.11±6.70%; p=0.011), whereas the difference in %VO between the two groups decreased at 24 months (20.88±5.72% vs 23.50±7.33%; p=0.24). There was no significant difference in percentage malapposed struts and percentage uncovered struts between the two groups at both time points.
Conclusions: In the serial comparative OCT analysis of the MiStent versus the XIENCE, the MiStent showed a more favourable efficacy for preventing neointimal formation with comparable strut tissue coverage, as compared with the XIENCE at six months, but this difference in %VO decreased at 24 months so that the difference in neointima at 24 months was no longer significant.
Conflict of interest statement
W. Wijns reports grants from Micell during the conduct of the study, grants from MicroPort, personal fees from Biotronik and Abbott Vascular, outside the submitted work, and being a co-founder of Argonauts, an innovation facilitator. P.W. Serruys reports personal fees from Abbott Laboratories, AstraZeneca, Biotronik, Cardialysis, GLG Research, Medtronic, Sino Medical Sciences Technology, Société Europa Digital & Publishing, Stentys France, Svelte Medical Systems, Philips/Volcano, St. Jude Medical, Qualimed, and Xeltis, outside the submitted work. The Guest Editor is a consultant for Edwards Lifesciences. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Räber L, Magro M, Stefanini GG, Kalesan B, van Domburg RT, Onuma Y, Wenaweser P, Daemen J, Meier B, Jüni P, Serruys PW, Windecker S. Very late coronary stent thrombosis of a newer-generation everolimus-eluting stent compared with early-generation drug-eluting stents: a prospective cohort study. Circulation. 2012;125:1110–21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.058560. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wijns W, Suttorp MJ, Zagozdzon L, Morice MC, McClean D, Stella P, Donohoe D, Knape C, Ormiston J. Evaluation of a crystalline sirolimus-eluting coronary stent with a bioabsorbable polymer designed for rapid dissolution: two-year outcomes from the DESSOLVE I and II trials. EuroIntervention. 2016;12:352–5. doi: 10.4244/EIJY15M09_14. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ormiston J, Webster M, Stewart J, Vrolix M, Whitbourn R, Donohoe D, Knape C, Lansky A, Attizzani G, Fitzgerald P, Kandzari DE, Wijns W. First-in-human evaluation of a bioabsorbable polymer-coated sirolimus-eluting stent: imaging and clinical results of the DESSOLVE I Trial (DES with sirolimus and a bioabsorbable polymer for the treatment of patients with de novo lesion in the native coronary arteries). JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6:1026–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2013.05.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lansky AJ, Kastrati A, Edelman ER, Parise H, Ng VG, Ormiston J, Wijns W, Byrne RA. Comparison of the Absorbable Polymer Sirolimus-Eluting Stent (MiStent) to the Durable Polymer Everolimus-Eluting Stent (Xience) (from the DESSOLVE I/II and ISAR-TEST-4 Studies). Am J Cardiol. 2016;117:532–8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2015.11.044. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

