The Extracellular Matrix Modulates the Metastatic Journey
- PMID: 31063753
- PMCID: PMC6527347
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.03.026
The Extracellular Matrix Modulates the Metastatic Journey
Abstract
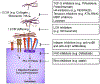
The extracellular matrix is perturbed in tumors. The tumor matrix promotes the growth, survival, and invasion of the cancer and modifies fibroblast and immune cell behavior to drive metastasis and impair treatment. Here, we discuss how the tumor matrix regulates metastasis by fostering tumor cell invasion into the stroma and migration toward the vasculature. We describe the role of the tumor matrix in cancer cell intravasation and vascular dissemination. We examine the impact of the matrix on disseminated tumor cell extravasation and on tumor dormancy and metastatic outgrowth. Finally, we discuss the clinical outcome of therapeutics that normalize tumor-matrix interactions.
Keywords: angiogenesis; dormancy; extracellular matrix; extravasation; integrin; intravasation; invasion; mechanics; mechanotransduction; metastasis; migration; outgrowth; pre-metastatic niche; tissue tension.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Afratis NA, Nikitovic D, Multhaupt HA, Theocharis AD, Couchman JR, and Karamanos NK (2017). Syndecans - key regulators of cell signaling and biological functions. FEBS J 284, 27–41. - PubMed
-
- Bando M (2016). Pirfenidone: Clinical trials and clinical practice in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Investig 54, 298–304. - PubMed
-
- Barbazan J, Alonso-Alconada L, Elkhatib N, Geraldo S, Gurchenkov V, Glentis A, van Niel G, Palmulli R, Fernandez B, Viano P, et al. (2017). Liver Metastasis Is Facilitated by the Adherence of Circulating Tumor Cells to Vascular Fibronectin Deposits. Cancer Res 77, 3431–3441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

