MiR-191 inhibit angiogenesis after acute ischemic stroke targeting VEZF1
- PMID: 31064890
- PMCID: PMC6535071
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.101948
MiR-191 inhibit angiogenesis after acute ischemic stroke targeting VEZF1
Abstract
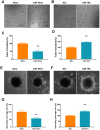
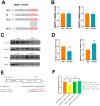
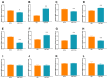
Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is a major public health problem in China. Impaired angiogenesis plays crucial roles in the development of ischemic cerebral injury. Recent studies have identified that microRNAs (miRNAs) are important regulators of angiogenesis, but little is known the exact effects of angiogenesis-associated miRNAs in AIS. In the present study, we detected the expression levels of angiogenesis-associated miRNAs in AIS patients, middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) rats, and oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). MiR-191 was increased in the plasma of AIS patients, OGD/R HUVECs, and the plasma and brain of MCAO rats. Over-expression of miR-191 promoted apoptosis, but reduced the proliferation, migration, tube-forming and spheroid sprouting activity in HUVECs OGD/R model. Mechanically, vascular endothelial zinc finger 1 (VEZF1) was identified as the direct target of miR-191, and could be regulated by miR-191 at post-translational level. In vivo studies applying miR-191 antagomir demonstrated that inhibition of miR-191 reduced infarction volume in MCAO rats. In conclusion, our data reveal a novel role of miR-191 in promoting ischemic brain injury through inhibiting angiogenesis via targeting VEZF1. Therefore, miR-191 may serve as a biomarker or a therapeutic target for AIS.
Keywords: VEZF1; acute stroke; angiogenesis factor; miR-191.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







References
-
- Wei JW, Heeley EL, Wang JG, Huang Y, Wong LK, Li Z, Heritier S, Arima H, Anderson CS, and ChinaQUEST Investigators. Comparison of recovery patterns and prognostic indicators for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in China: the ChinaQUEST (QUality Evaluation of Stroke Care and Treatment) Registry study. Stroke. 2010; 41:1877–83. 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.586909 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, Biller J, Brown M, Demaerschalk BM, Hoh B, Jauch EC, Kidwell CS, Leslie-Mazwi TM, et al., and American Heart Association Stroke Council. 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2018; 49:e46–110. 10.1161/STR.0000000000000158 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Licata G, Tuttolomondo A, Corrao S, Di Raimondo D, Fernandez P, Caruso C, Avellone G, Pinto A. Immunoinflammatory activation during the acute phase of lacunar and non-lacunar ischemic stroke: association with time of onset and diabetic state. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2006; 19:639–46. 10.1177/039463200601900320 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tuttolomondo A, Di Sciacca R, Di Raimondo D, Pedone C, La Placa S, Pinto A, Licata G. Effects of clinical and laboratory variables and of pretreatment with cardiovascular drugs in acute ischaemic stroke: a retrospective chart review from the GIFA study. Int J Cardiol. 2011; 151:318–22. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2010.06.005 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

