GBA and APOE ε4 associate with sporadic dementia with Lewy bodies in European genome wide association study
- PMID: 31065058
- PMCID: PMC6504850
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-43458-2
GBA and APOE ε4 associate with sporadic dementia with Lewy bodies in European genome wide association study
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: GBA and APOE ε4 associate with sporadic dementia with Lewy bodies in European genome wide association study.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 17;9(1):15168. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51827-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31619746 Free PMC article.
Abstract
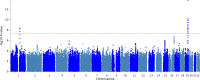
Dementia with Lewy Bodies (DLB) is a common neurodegenerative disorder with poor prognosis and mainly unknown pathophysiology. Heritability estimates exceed 30% but few genetic risk variants have been identified. Here we investigated common genetic variants associated with DLB in a large European multisite sample. We performed a genome wide association study in Norwegian and European cohorts of 720 DLB cases and 6490 controls and included 19 top-associated single-nucleotide polymorphisms in an additional cohort of 108 DLB cases and 75545 controls from Iceland. Overall the study included 828 DLB cases and 82035 controls. Variants in the ASH1L/GBA (Chr1q22) and APOE ε4 (Chr19) loci were associated with DLB surpassing the genome-wide significance threshold (p < 5 × 10-8). One additional genetic locus previously linked to psychosis in Alzheimer's disease, ZFPM1 (Chr16q24.2), showed suggestive association with DLB at p-value < 1 × 10-6. We report two susceptibility loci for DLB at genome-wide significance, providing insight into etiological factors. These findings highlight the complex relationship between the genetic architecture of DLB and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Arvid Rongve, Aree Witoelar, Agustín Ruiz, Lavinia Athanasiu, Carla Abdelnour, Jordi Clarimon, Stefanie Heilmann-Heimbach, Isabel Hernández, Sonia Moreno-Grau, Itziar de Rojas, Estrella Morenas-Rodríguez, Tormod Fladbym, Sigrid B. Sando, Geir Bråthen, Frédéric Blanc, Olivier Bousiges, Afina W. Lemstra, Inger van Steenoven, Elisabet Londos, Ina S. Almdahl, Lene Pålhaugen, Jon A. Eriksen, Srdjan Djurovic, Eystein Stordal, Ingvild Saltvedt, Ingun D. Ulstein, Francesco Bettella, Rahul S. Desikan, Ane-Victoria Idland, Mathias Toft, Lasse Pihlstrøm, Jon Snaedal, Lluís Tárraga, Mercè Boada, Alberto Lleó and Alfredo Ramírez declare no competing interests. Kári Stefánsson and Hreinn Stefánsson are employees of deCODE Genetics, Iceland. Ole A. Andreassen has received speaker’s honorarium from Lundbeck and has a pending patent for biostatistical genetic methodology. Dr Aarsland has received research support and/or honoraria from Astra-Zeneca, H. Lundbeck, Novartis Pharmaceuticals and GE Health, and served as paid consultant for H. Lundbeck, Eisai, Heptares, Safnoi, Mentis Cura. Dag Aarsland is a Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award Holder and would like to thank the Wolfson Foundation and the Royal Society for their support.
Figures
References
-
- Svendsboe E, et al. Caregiver burden in family carers of people with dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2016;31:1075–1083. - PubMed
-
- Bjoerke-Bertheussen J, Ehrt U, Rongve A, Ballard C, Aarsland D. Neuropsychiatric symptoms in mild dementia with lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2012;34:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Oesterhus R, et al. Long-term mortality in a cohort of home-dwelling elderly with mild Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2014;38:161–169. - PubMed
-
- Rongve A, Vossius C, Nore S, Testad I, Aarsland D. Time until nursing home admission in people with mild dementia: comparison of dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2014;29:392–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

