[Rare localization of lipoma in the parotid region: about a case]
- PMID: 31065314
- PMCID: PMC6488243
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2018.31.154.14605
[Rare localization of lipoma in the parotid region: about a case]
Abstract
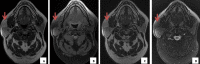
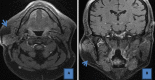
Lipomas localization in the parotid region is very rare. We here report a new case of a 55-year old patient, presenting with a mass in the parotid region that had progressed over the past 4 years and a literature review. A soft, mobile and painless mass was detected on palpation. The patient underwent imaging examinations (ultrasound and MRI), that enabled to retain the diagnosis of parotid lipoma. The patient decided to have conservative treatment.
La localisation des lipomes au niveau parotidien est très rare. Nous rapportons un nouveau cas avec une revue de littérature concernant un patient de 55 ans, qui a consulté pour une masse au niveau de la région parotidienne évoluant depuis quatre ans. À la palpation nous avons trouvé une formation de consistance molle, mobile et indolore. Le patient a bénéficié par la suite d'une imagerie (échographie et IRM), d'où le diagnostic final d'un lipome parotidien a été retenu ; le traitement était conservateur sur le choix du patient.
Keywords: IRM cérébrale; Lipome; parotide.
Conflict of interest statement
Les auteurs ne déclarent aucun conflit d’intérêts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Huge lipoma of the right parotid gland: Case report and review of 42 cases.Ear Nose Throat J. 2016 Jan;95(1):E8-E13. doi: 10.1177/014556131609500103. Ear Nose Throat J. 2016. PMID: 26829698 Review.
-
A case of lipoma of the deep lobe of the parotid gland.Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2003 Apr;10(4):167-70. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg. 2003. PMID: 12941989
-
Lipoma of the parotid gland.J Korean Med Sci. 1996 Dec;11(6):522-5. doi: 10.3346/jkms.1996.11.6.522. J Korean Med Sci. 1996. PMID: 9008102 Free PMC article.
-
[Deep lobe parotid gland lipoma: an extremely rare entity. A case report].Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2006 Jun;51(3):239-42. doi: 10.1016/j.anplas.2005.12.008. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2006. PMID: 16519982 French.
-
Congenital sialolipoma of parotid gland: a report of rare and recently described entity with review of literature.Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2007 May-Jun;10(3):244-6. doi: 10.2350/06-09-0170.1. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17535092 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Baker SE, Jensen JL, Correll RW. Lipomas of the parotid gland. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1981;52(3):167–7. - PubMed
-
- Houston GD, Brannon RB. Lipoma of the parotid gland. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1985;60(5):72–4. - PubMed
-
- Kimura Y, Ischikawa N, Goutsu K, Kitamura K, Kishimoto S. Lipoma in the deep lobe of the parotid gland: a case report. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2002;29:391–3. - PubMed
-
- Barnes L. Tumours and tumour like lesions in head and neck, In: Surgical pathology of head and neck. 1. Vol. 56. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc; 1985. pp. 747–58.
-
- Srinivasan V, Ganesan S, Premachandra J. Lipoma of the parotid gland presenting with facial palsy. J Laryngol Otol. 1996;110(2):93–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
