Celiac disease-on-chip: Modeling a multifactorial disease in vitro
- PMID: 31065364
- PMCID: PMC6488795
- DOI: 10.1177/2050640619836057
Celiac disease-on-chip: Modeling a multifactorial disease in vitro
Abstract
Conventional model systems cannot fully recapitulate the multifactorial character of complex diseases like celiac disease (CeD), a common chronic intestinal disorder in which many different genetic risk factors interact with environmental factors such as dietary gluten. However, by combining recently developed human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) technology and organ-on-chip technology, in vitro intestine-on-chip systems can now be developed that integrate the genetic background of complex diseases, the different interacting cell types involved in disease pathology, and the modulating environmental factors such as gluten and the gut microbiome. The hiPSCs that are the basis of these systems can be generated from both diseased and healthy individuals, which means they can be stratified based on their load of genetic risk factors. A CeD-on-chip model system has great potential to improve our understanding of disease etiology and accelerate the development of novel treatments and preventive therapies in CeD and other complex diseases.
Keywords: Celiac disease; complex diseases; hiPSCs; human induced pluripotent stem cells; microfluidic devices; organ-on-chip.
Figures
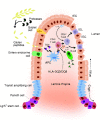




References
-
- Biagi F, Klersy C, Balduzzi D, et al. Are we not over-estimating the prevalence of coeliac disease in the general population?. Ann Med 2010; 42: 557–561. - PubMed
-
- Caminero A, Galipeau HJ, McCarville JL, et al. Duodenal bacteria from patients with celiac disease and healthy subjects distinctly affect gluten breakdown and immunogenicity. Gastroenterology 2016; 151: 670–683. - PubMed
-
- Spijkerman M, Tan IL, Kolkman JL, et al. A large variety of clinical features and concomitant disorders in celiac disease—A cohort study in the Netherlands. Dig Liver Dis 2016; 48: 499–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

