CYP2C11 played a significant role in down-regulating rat blood pressure under the challenge of a high-salt diet
- PMID: 31065462
- PMCID: PMC6485204
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.6807
CYP2C11 played a significant role in down-regulating rat blood pressure under the challenge of a high-salt diet
Abstract
Background: Arachidonic acid (AA) is oxidized by cytochrome P450s (CYPs) to form epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs), compounds that modulate ion transport, gene expression, and vasorelaxation. Both CYP2Cs and CYP2Js are involved in kidney EET epoxidation.
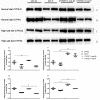
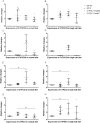
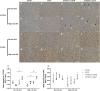
Methods: In this study, we used a CYP2C11-null rat model to explore the in vivo effects of CYP2C11 on vasorelaxation. For 2 months, CYP2C11-null and wild-type (WT) Sprague-Dawley rats were either fed normal lab (0.3% (w/w) sodium chloride) or high-salt (8% (w/w) sodium chloride) diets. Subsequently, an invasive method was used to determine blood pressure. Next, western blots, quantitative PCR, and immunohistochemistry were used to determine renal expression of CYPs involved in AA metabolism.
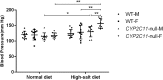
Results: Among CYP2C11-null rats, a high-salt diet (females: 156.79 ± 15.89 mm Hg, males: 130.25 ± 16.76 mm Hg, n = 10) resulted in significantly higher blood pressure than a normal diet (females: 118.05 ± 8.43 mm Hg, P < 0.01; males: 115.15 ± 11.45 mm Hg, P < 0.05, n = 10). Compared with WT rats under the high-salt diet, western blots showed that CYP2C11-null rats had higher renal expression of CYP2J2 and CYP4A. This was consistent with the results of immunohistochemistry and the qPCR, respectively. The two rat strains did not differ in the renal expression of CYP2C23 or CYP2C24.
Conclusion: Our findings suggested that CYP2C11 plays an important role in lowering blood pressure under the challenge of a high-salt diet.
Keywords: Blood pressure; CYP2C11-null rats; CYP2J2; Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; High-salt diet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal epoxyeicosatrienoic acid synthesis during pregnancy.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Jan;288(1):F221-6. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00170.2004. Epub 2004 Sep 21. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15383399
-
Decreased renal cytochrome P450 2C enzymes and impaired vasodilation are associated with angiotensin salt-sensitive hypertension.Hypertension. 2003 Mar;41(3 Pt 2):709-14. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000047877.36743.FA. Epub 2002 Dec 16. Hypertension. 2003. PMID: 12623984
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid inhibition alters renal hemodynamics during pregnancy.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2006 Dec;231(11):1744-52. doi: 10.1177/153537020623101112. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2006. PMID: 17138762
-
Purinoceptors in renal microvessels: adenosine-activated and cytochrome P450 monooxygenase-derived arachidonate metabolites.Pharmacol Rep. 2005;57 Suppl:191-5. Pharmacol Rep. 2005. PMID: 16415499 Review.
-
Role of cytochrome P450-dependent arachidonic acid metabolites in liver physiology and pathophysiology.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2003 Oct;72(1-2):51-71. doi: 10.1016/s1098-8823(03)00077-7. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2003. PMID: 14626496 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment and characterization of liver-specific Apoa4-Cre and Cyp2c11-Cre rat models in juvenile and adult stages.Animal Model Exp Med. 2025 Apr;8(4):718-727. doi: 10.1002/ame2.12504. Epub 2025 Feb 6. Animal Model Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 39916324 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-Cas9: A method for establishing rat models of drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Oct;11(10):2973-2982. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.01.007. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 34745851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acclimation to a High-Salt Diet Is Sex Dependent.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 Mar;11(5):e020450. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.020450. Epub 2022 Feb 22. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35191321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrosius WT, Sink KM, Foy CG, Berlowitz DR, Cheung AK, Cushman WC, Fine LJ, Goff DC, Jr, Johnson KC, Killeen AA, Lewis CE, Oparil S, Reboussin DM, Rocco MV, Snyder JK, Williamson JD, Wright JT, Jr, Whelton PK, The SPRINT Study Research Group The design and rationale of a multicenter clinical trial comparing two strategies for control of systolic blood pressure: the systolic blood pressure intervention trial (SPRINT) Clinical Trials: Journal of the Society for Clinical Trials. 2014;11(5):532–546. doi: 10.1177/1740774514537404. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Capdevila J, Falck J, Harris RC. Cytochrome P450 and arachidonic acid bioactivation. Molecular and functional properties of the arachidonate monooxygenase. Journal of Lipid Research. 2000;41(2):163–181. - PubMed
-
- Capdevila JH, Pidkovka N, Mei S, Gong Y, Falck JR, Imig JD, Harris RC, Wang W. The Cyp2c44 epoxygenase regulates epithelial sodium channel activity and the blood pressure responses to increased dietary salt. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2014;289(7):4377–4386. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.508416. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

