The Hippo Pathway Blocks Mammalian Retinal Müller Glial Cell Reprogramming
- PMID: 31067451
- PMCID: PMC6521882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.047
The Hippo Pathway Blocks Mammalian Retinal Müller Glial Cell Reprogramming
Abstract
In response to retinal damage, the Müller glial cells (MGs) of the zebrafish retina have the ability to undergo a cellular reprogramming event in which they enter the cell cycle and divide asymmetrically, thereby producing multipotent retinal progenitors capable of regenerating lost retinal neurons. However, mammalian MGs do not exhibit such a proliferative and regenerative ability. Here, we identify Hippo pathway-mediated repression of the transcription cofactor YAP as a core regulatory mechanism that normally blocks mammalian MG proliferation and cellular reprogramming. MG-specific deletion of Hippo pathway components Lats1 and Lats2, as well as transgenic expression of a Hippo non-responsive form of YAP (YAP5SA), resulted in dramatic Cyclin D1 upregulation, loss of adult MG identity, and attainment of a highly proliferative, progenitor-like cellular state. Our results reveal that mammalian MGs may have latent regenerative capacity that can be stimulated by repressing Hippo signaling.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; LATS; Müller glia; YAP; regeneration; reprogramming; retina.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
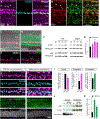

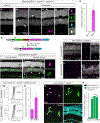
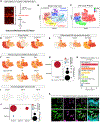
References
-
- Azzolin L, Zanconato F, Bresolin S, Forcato M, Basso G, Bicciato S, Cordenonsi M, and Piccolo S (2012). Role of TAZ as mediator of Wnt signaling. Cell 151, 1443–1456. - PubMed
-
- Azzolin L, Panciera T, Soligo S, Enzo E, Bicciato S, Dupont S, Bresolin S, Frasson C, Basso G, Guzzardo V, et al. (2014). YAP/TAZ incorporation in the β-catenin destruction complex orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell 158, 157–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL118761/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127717/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY030448/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036211/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006348/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY024906/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL136065/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006348/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL130804/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR024574/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE023177/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

