All-optical spiking neurosynaptic networks with self-learning capabilities
- PMID: 31068721
- PMCID: PMC6522354
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1157-8
All-optical spiking neurosynaptic networks with self-learning capabilities
Abstract
Software implementations of brain-inspired computing underlie many important computational tasks, from image processing to speech recognition, artificial intelligence and deep learning applications. Yet, unlike real neural tissue, traditional computing architectures physically separate the core computing functions of memory and processing, making fast, efficient and low-energy computing difficult to achieve. To overcome such limitations, an attractive alternative is to design hardware that mimics neurons and synapses. Such hardware, when connected in networks or neuromorphic systems, processes information in a way more analogous to brains. Here we present an all-optical version of such a neurosynaptic system, capable of supervised and unsupervised learning. We exploit wavelength division multiplexing techniques to implement a scalable circuit architecture for photonic neural networks, successfully demonstrating pattern recognition directly in the optical domain. Such photonic neurosynaptic networks promise access to the high speed and high bandwidth inherent to optical systems, thus enabling the direct processing of optical telecommunication and visual data.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
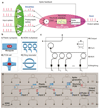
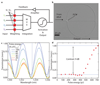
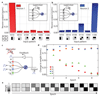
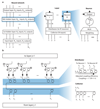
Comment in
-
A role for optics in AI hardware.Nature. 2019 May;569(7755):199-200. doi: 10.1038/d41586-019-01406-0. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31068716 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lane ND, et al. Squeezing Deep Learning into Mobile and Emdedded Devices. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2017;16:82–88.
-
- Amato F, et al. Artificial neural networks in medical diagnosis. J Appl Biomed. 2013;11:47–58.
-
- Nawrocki RA, Voyles RM, Shaheen SE. A Mini Review of Neuromorphic Architectures and Implementations. IEEE Trans Electron Devices. 2016;63:3819–3829.
-
- Preissl R, et al. Compass: A scalable simulator for an architecture for cognitive computing. Int Conf High Perform Comput Networking, Storage Anal SC; 2012.
-
- von Neumann J. The Computer and The Brain. Yale University Press; 1958.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

