Moving Health Upstream in Urban Development: Reflections on the Operationalization of a Transdisciplinary Case Study
- PMID: 31069111
- PMCID: PMC6450444
- DOI: 10.1002/gch2.201700103
Moving Health Upstream in Urban Development: Reflections on the Operationalization of a Transdisciplinary Case Study
Abstract
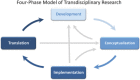
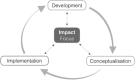
This paper describes the development, conceptualization, and implementation of a transdisciplinary research pilot, the aim of which is to understand how human and planetary health could become a priority for those who control the urban development process. Key challenges include a significant dislocation between academia and the real world, alongside systemic failures in valuation and assessment mechanisms. The National Institutes of Health four-phase model of transdisciplinary team-based research is drawn on and adapted to reflect on what has worked well and what has not operationally. Results underscore the need for experienced academics open to new collaborations and ways of working; clarity of leadership without compromising exploration; clarification of the poorly understood "impacts interface" and navigation toward effective real world impact; acknowledgement of the additional time and resource required for transdisciplinary research and "nonacademic" researchers. Having practitioner-researchers as part of the research leadership team requires rigourous reflective practice and effective management, but it can also ensure breadth in transdisciplinary outlook as well as constant course correction toward real-world impact. It is important for the research community to understand better the opportunities and limitations provided by knowledge intermediaries in terms of function, specialism, and experience.
Keywords: impact; planetary health; transdisciplinary; upstream; urbanization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization , Global Report on Urban Health: Equitable, Healthier Cities for Sustainable Development, WHO, Geneva: 2016.
-
- Whitmee S., Haines A., Beyrer C., Boltz F., Capon A., Ferreira de Souza Dias B., Ezeh A., Frumkin H., Gong P., Head P., Horton R., Mace G., Marten R., Myers S., Nishtar S., Osofsky S., Pattanayak S., Pongsiri M., Romanelli C., Soucat A., Vega J., Yach D., Lancet; 2015, 386, 1973. - PubMed
-
- Dannenberg A., Frumkin H., Jackson R., Making Healthy Places—Designing and Building for Health, Well‐Being and Sustainability, Island Press, Washington: 2011.
-
- Lawrence R., Futures 2004, 36, 487.
-
- LSE Public Policy Group , Maximising the impacts of your research: a handbook for social scientists, http://blogs.lse.ac.uk/impactofsocialsciences/2011/04/14/maximizing‐the‐... (accessed: October 2017).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

