Gene Therapy Leaves a Vicious Cycle
- PMID: 31069169
- PMCID: PMC6491712
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00297
Gene Therapy Leaves a Vicious Cycle
Abstract
The human genetic code encrypted in thousands of genes holds the secret for synthesis of proteins that drive all biological processes necessary for normal life and death. Though the genetic ciphering remains unchanged through generations, some genes get disrupted, deleted and or mutated, manifesting diseases, and or disorders. Current treatment options-chemotherapy, protein therapy, radiotherapy, and surgery available for no more than 500 diseases-neither cure nor prevent genetic errors but often cause many side effects. However, gene therapy, colloquially called "living drug," provides a one-time treatment option by rewriting or fixing errors in the natural genetic ciphering. Since gene therapy is predominantly a viral vector-based medicine, it has met with a fair bit of skepticism from both the science fraternity and patients. Now, thanks to advancements in gene editing and recombinant viral vector development, the interest of clinicians and pharmaceutical industries has been rekindled. With the advent of more than 12 different gene therapy drugs for curing cancer, blindness, immune, and neuronal disorders, this emerging experimental medicine has yet again come in the limelight. The present review article delves into the popular viral vectors used in gene therapy, advances, challenges, and perspectives.
Keywords: clinical trials; diseases and disorders; gene therapy; modern medicines; viral vectors.
Figures
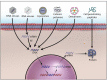


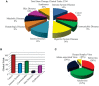
References
-
- Omenn GS, Lane L, Lundberg EK, Beavis RC, Overall CM, Deutsch EW. Metrics for the Human Proteome Project 2016: progress on identifying and characterizing the human proteome, including post-translational modifications. J Proteome Res. (2016) 15:3951–60. 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00511 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

