Resistance and clonal selection among Allium sativum L. germplasm resources to Delia antiqua M. and its correlation with allicin content
- PMID: 31069939
- PMCID: PMC6771725
- DOI: 10.1002/ps.5478
Resistance and clonal selection among Allium sativum L. germplasm resources to Delia antiqua M. and its correlation with allicin content
Abstract
Background: Garlic is the second largest allium crop after onion and is grown all over the world. The onion maggot (Delia antiqua M.) is a pest that seriously affects the yield and quality of garlic. Cultural controls and insecticides have several potential problems, including pesticide residue and development of resistance. Screening resistant varieties is an ideal alternative method.
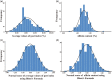
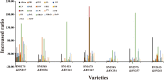
Results: The resistance of 213 accessions of garlic clones against onion maggot was identified. The results showed that the pest index was between 5.56% and 91.11%, with classification into six groups by cluster analysis: HR (highly resistant), R (resistant), MR (moderately resistant), MS (moderately susceptible), S (susceptible) and HS (highly susceptible). Among these accessions, 9 and 30 were HR and R to onion maggot, respectively. Comparing the resistances of seven pairs of accessions between the original accessions and their progenies showed that single bulb clonal selection could be an effective way to improve allicin content, onion maggot resistance and most morphological traits. The relationship between allicin content and resistance was investigated, and a significant positive relationship was found. Accessions with a high content of allicin have great potential as resistant accessions.
Conclusion: This study showed significant differences among garlic germplasm in their response to Delia antiqua M. Some accessions were highly resistant and tolerant. Utilization of these accessions will help minimize environmental pollution, preserve agro-ecosystems and biodiversity, and make management processes more economical. Furthermore, these accessions could be used in breeding programs to develop new maggot-resistant onion cultivars. © 2019 The Authors. Pest Management Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society of Chemical Industry.
Keywords: Allium sativum L.; Delia antiqua M.; allicin; garlic; onion maggot; resistance.
© 2019 The Authors. Pest Management Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Society of Chemical Industry.
Figures



References
-
- Vavilov NI, The origin, variation, immunity and breeding of cultivated plants. Soil Sci 72:482 (1951).
-
- Etoh T, Watanabe H and Iwai S, RAPD variation of garlic clones in the center of origin and the westernmost area of distribution. Mem Fac Agric Kogoshima Univ 37:21–27 (2001).
-
- Wang H, Li X, Shen D, Yang O and Song J, Diversity evaluation of morphological traits and allicin content in garlic (Allium sativum L.) from China. Euphytica 198:243–254 (2014).
-
- Wang H, Li X, Liu X, Oiu Y, Song J and Zhang X, Genetic diversity of garlic (Allium sativum L.) germplasm from China by fluorescent‐based AFLP, SSR and InDel markers. Plant Breeding 135:743–750 (2016).
-
- Srivastava SC, Sharma UC, Singh BK and Yadava HS, A profile of garlic production in India: facts, trends and opportunities. Int J Agric Environ Biotechnol 5:477–482 (2012).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- The Key Laboratory of Biology and Genetic Improvement of Horticultural Crops, Ministry of Agriculture, People's Republic of China,
- 2016YFD0100204-8/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- IVF-BRF2018001/IVF Basic Research Project
- 31872946/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CARS-24-A-01/National Program of Characteristics of Vegetable Industry Technology System
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

