NIMH MonkeyLogic: Behavioral control and data acquisition in MATLAB
- PMID: 31071345
- PMCID: PMC6743332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2019.05.002
NIMH MonkeyLogic: Behavioral control and data acquisition in MATLAB
Abstract
Background: Computerized control of behavioral paradigms is an essential element of neurobehavioral studies, especially physiological recording studies that require sub-millisecond precision. Few software solutions provide a simple, flexible environment to create and run these applications. MonkeyLogic, a MATLAB-based package, was developed to meet these needs, but faces a performance crisis and obsolescence due to changes in MATLAB itself.
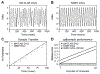
New method: Here we report a complete redesign and rewrite of MonkeyLogic, now NIMH MonkeyLogic, that natively supports the latest 64-bit MATLAB on the Windows platform. Major layers of the underlying real-time hardware control were removed and replaced by custom toolboxes: NIMH DAQ Toolbox and MonkeyLogic Graphics Library. The redesign resolves undesirable delays in data transfers and limitations in graphics capabilities.
Results: NIMH MonkeyLogic is essentially a new product. It provides a powerful new scripting framework, has dramatic speed enhancements and provides major new graphics abilities.
Comparison with existing method: NIMH MonkeyLogic is fully backward compatible with earlier task scripts, but with better temporal precision. It provides more input device options, superior graphics and a new real-time closed-loop programming model. Because NIMH MonkeyLogic requires no commercial toolbox and has a reduced hardware requirement, implementation costs are substantially reduced.
Conclusion: NIMH MonkeyLogic is a versatile, powerful, up-to-date tool for controlling a wide range of experiments. It is freely available from https://monkeylogic.nimh.nih.gov/.
Keywords: Cognition; Human; Monkey; Neurophysiology; Psychophysics; Software.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures



References
-
- Acquiring high-resolution time stamps [WWW Document], 2018. Microsoft Docs. URL https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/desktop/SysInfo/acquiring-high-... (accessed 12.6.18).
-
- Brainard DH, 1997. The Psychophysics Toolbox. Spat. Vis 10, 433–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

