Molecular Mechanisms of Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Lung: Clinical and Experimental Perspectives
- PMID: 31071959
- PMCID: PMC6540248
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20092272
Molecular Mechanisms of Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Lung: Clinical and Experimental Perspectives
Abstract
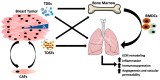
Breast cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in women worldwide, and >90% of breast cancer-related deaths are associated with metastasis. Breast cancer spreads preferentially to the lung, brain, bone and liver; termed organ tropism. Current treatment methods for metastatic breast cancer have been ineffective, compounded by the lack of early prognostic/predictive methods to determine which organs are most susceptible to developing metastases. A better understanding of the mechanisms that drive breast cancer metastasis is crucial for identifying novel biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Lung metastasis is of particular concern as it is associated with significant patient morbidity and a mortality rate of 60-70%. This review highlights the current understanding of breast cancer metastasis to the lung, including discussion of potential new treatment approaches for development.
Keywords: breast cancer; exosomes; lung metastasis; pre-metastatic niche; targeted therapies; tumor secreted factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Canadian Cancer Society. [(accessed on 2 January 2019)]; Available online: http://www.cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-type/breast/statistics....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

