Widespread Existence of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors in Marine Bacteria: Potential Drugs to Combat Pathogens with Novel Strategies
- PMID: 31072008
- PMCID: PMC6562741
- DOI: 10.3390/md17050275
Widespread Existence of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors in Marine Bacteria: Potential Drugs to Combat Pathogens with Novel Strategies
Abstract
Quorum sensing (QS) is a phenomenon of intercellular communication discovered mainly in bacteria. A QS system consisting of QS signal molecules and regulatory protein components could control physiological behaviors and virulence gene expression of bacterial pathogens. Therefore, QS inhibition could be a novel strategy to combat pathogens and related diseases. QS inhibitors (QSIs), mainly categorized into small chemical molecules and quorum quenching enzymes, could be extracted from diverse sources in marine environment and terrestrial environment. With the focus on the exploitation of marine resources in recent years, more and more QSIs from the marine environment have been investigated. In this article, we present a comprehensive review of QSIs from marine bacteria. Firstly, screening work of marine bacteria with potential QSIs was concluded and these marine bacteria were classified. Afterwards, two categories of marine bacteria-derived QSIs were summarized from the aspects of sources, structures, QS inhibition mechanisms, environmental tolerance, effects/applications, etc. Next, structural modification of natural small molecule QSIs for future drug development was discussed. Finally, potential applications of QSIs from marine bacteria in human healthcare, aquaculture, crop cultivation, etc. were elucidated, indicating promising and extensive application perspectives of QS disruption as a novel antimicrobial strategy.
Keywords: QS inhibition mechanisms; QS inhibitors; application; marine bacteria; quorum quenching enzymes; small molecule QS inhibitors; structural modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
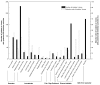
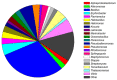
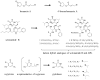
Similar articles
-
Bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors: attractive alternatives for control of infectious pathogens showing multiple drug resistance.Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2013 Apr;8(1):68-83. doi: 10.2174/1574891x11308010012. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23394143 Review.
-
Quorum sensing: A less known mode of communication among fungi.Microbiol Res. 2018 May;210:51-58. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2018.03.007. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Microbiol Res. 2018. PMID: 29625658 Review.
-
Quorum Sensing Inhibitors from Marine Microorganisms and Their Synthetic Derivatives.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jan 28;17(2):80. doi: 10.3390/md17020080. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30696031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum sensing: a new prospect for the management of antimicrobial-resistant infectious diseases.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021 May;19(5):571-586. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2021.1843427. Epub 2020 Dec 8. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2021. PMID: 33131352 Review.
-
Mechanisms of quorum sensing and strategies for quorum sensing disruption in aquaculture pathogens.J Fish Dis. 2015 Sep;38(9):771-86. doi: 10.1111/jfd.12299. Epub 2014 Sep 15. J Fish Dis. 2015. PMID: 25219871 Review.
Cited by
-
Marine Pharmacology in 2019-2021: Marine Compounds with Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, Antifungal, Anti-Inflammatory, Antiprotozoal, Antituberculosis and Antiviral Activities; Affecting the Immune and Nervous Systems, and Other Miscellaneous Mechanisms of Action.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jun 30;22(7):309. doi: 10.3390/md22070309. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39057418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum Quenching in a Novel Acinetobacter sp. XN-10 Bacterial Strain against Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum.Microorganisms. 2020 Jul 23;8(8):1100. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8081100. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32717872 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis on discovering anti-quorum sensing agents against clinically relevant pathogens: current status, development, and future directions.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 30;14:1297843. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1297843. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38098670 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Sensing Inhibition by Marine Bacteria.Mar Drugs. 2019 Jul 23;17(7):427. doi: 10.3390/md17070427. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31340463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the Diversity and Biomedical Potential of Microbes Associated With the Neptune's Cup Sponge, Cliona patera.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 29;12:631445. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.631445. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34267732 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

