Consumption of Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice with or without Vitamin C Supplementation Increases the Excretion of Urinary Nitrate, Nitrite, and N-nitroso Compounds in Humans
- PMID: 31072023
- PMCID: PMC6539140
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20092277
Consumption of Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice with or without Vitamin C Supplementation Increases the Excretion of Urinary Nitrate, Nitrite, and N-nitroso Compounds in Humans
Abstract
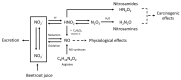
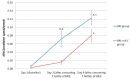
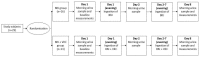
Consumption of nitrate-rich beetroot juice (BRJ) by athletes induces a number of beneficial physiological health effects, which are linked to the formation of nitric oxide (NO) from nitrate. However, following a secondary pathway, NO may also lead to the formation of N-nitroso compounds (NOCs), which are known to be carcinogenic in 39 animal species. The extent of the formation of NOCs is modulated by various other dietary factors, such as vitamin C. The present study investigates the endogenous formation of NOCs after BRJ intake and the impact of vitamin C on urinary NOC excretion. In a randomized, controlled trial, 29 healthy recreationally active volunteers ingested BRJ with or without additional vitamin C supplements for one week. A significant increase of urinary apparent total N-nitroso Compounds (ATNC) was found after one dose (5 to 47 nmol/mmol: p < 0.0001) and a further increase was found after seven consecutive doses of BRJ (104 nmol/mmol: p < 0.0001). Vitamin C supplementation inhibited ATNC increase after one dose (16 compared to 72 nmol/mmol, p < 0.01), but not after seven daily doses. This is the first study that shows that BRJ supplementation leads to an increase in formation of potentially carcinogenic NOCs. In order to protect athlete's health, it is therefore important to be cautious with chronic use of BRJ to enhance sports performances.
Keywords: Beetroot juice; N-nitroso compounds; human dietary intervention; nitrate; nitrite; vitamin C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Oral Supplementation With Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice in Patients With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension-Results From BEET-PAH, an Exploratory Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Crossover Study.J Card Fail. 2018 Oct;24(10):640-653. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2018.09.010. Epub 2018 Sep 20. J Card Fail. 2018. PMID: 30244181 Clinical Trial.
-
The benefits and risks of beetroot juice consumption: a systematic review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021;61(5):788-804. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1746629. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 32292042
-
No Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on 100-m and 200-m Swimming Performance in Moderately Trained Swimmers.Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019 Jul 1;14(6):706-710. doi: 10.1123/ijspp.2018-0654. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. 2019. PMID: 30427246 Clinical Trial.
-
Acute Supplementation with Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice Causes a Greater Increase in Plasma Nitrite and Reduction in Blood Pressure of Older Compared to Younger Adults.Nutrients. 2019 Jul 22;11(7):1683. doi: 10.3390/nu11071683. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31336633 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nitrate ingestion: a review of the health and physical performance effects.Nutrients. 2014 Nov 18;6(11):5224-64. doi: 10.3390/nu6115224. Nutrients. 2014. PMID: 25412154 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diet in neurogenic bowel management: A viewpoint on spinal cord injury.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 May 28;26(20):2479-2497. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i20.2479. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32523306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acceptability and Feasibility of a 13-Week Pilot Randomised Controlled Trial Testing the Effects of Incremental Doses of Beetroot Juice in Overweight and Obese Older Adults.Nutrients. 2021 Feb 26;13(3):769. doi: 10.3390/nu13030769. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33653009 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Beet supplementation mitigates post-exercise inflammation.Front Nutr. 2024 May 30;11:1408804. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1408804. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38873567 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Combined Inorganic Nitrate and Nitrite Supplementation on Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Skeletal Muscle Oxidative Capacity in Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 25;14(21):4479. doi: 10.3390/nu14214479. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36364742 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Beetroot as a functional food with huge health benefits: Antioxidant, antitumor, physical function, and chronic metabolomics activity.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Sep 9;9(11):6406-6420. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2577. eCollection 2021 Nov. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34760270 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bailey S.J., Winyard P., Vanhatalo A., Blackwell J.R., Dimenna F.J., Wilkerson D.P., Tarr J., Benjamin N., Jones A.M. Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of low-intensity exercise and enhances tolerance to high-intensity exercise in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009;107:1144–1155. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00722.2009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

