Anti-PD-1 Antibody Administration following Hip Fracture Surgery Reverses Immune Dysfunction and Decreases Susceptibility to Infection
- PMID: 31073275
- PMCID: PMC6470458
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8492090
Anti-PD-1 Antibody Administration following Hip Fracture Surgery Reverses Immune Dysfunction and Decreases Susceptibility to Infection
Abstract
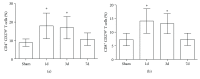
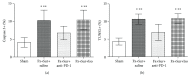
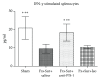
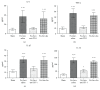
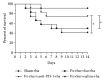
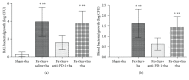
The aim of this investigation was to assess expression of programmed death-1 (PD-1) and inflammatory status after hip fracture surgery in aged mice and to evaluate the effect of anti-PD-1 antibody intervention. Male C57BL/6 mice aged 22-28 months underwent hip fracture and femoral intramedullary pinning or a sham procedure. Expression of PD-1 was measured on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Additionally, the effects of anti-PD-1 antibody on lymphocyte apoptosis, cytokine production, bacterial clearance, and survival were determined. Expression of PD-1 on T cells was upregulated in mice after hip fracture and surgery compared to sham controls. Administration of anti-PD-1 antibody prevented T lymphocyte apoptosis, increased IFN-γ production in splenocytes, and decreased systemic inflammation. Antibody blockade of PD-1 significantly decreased susceptibility to bacteria and improved survival rates of aged mice after hip fracture and surgery followed by the induction of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. This study showed that hip fracture and surgical trauma cause significant increases in PD-1 expression in aged mice. Antibody blockade of PD-1 partially reverses T cell apoptosis, decreases the systemic inflammatory response and susceptibility to bacteria, and reduces mortality.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined Trabectedin and anti-PD1 antibody produces a synergistic antitumor effect in a murine model of ovarian cancer.J Transl Med. 2015 Jul 29;13:247. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0613-y. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26219551 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of interferon-α-transduced tumor cell vaccines and blockade of programmed cell death-1 on the growth of established tumors.Cancer Gene Ther. 2012 Sep;19(9):637-43. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2012.42. Epub 2012 Jul 13. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22790963
-
Transient immunological and clinical effectiveness of treating mice bearing premalignant oral lesions with PD-1 antibodies.Int J Cancer. 2017 Apr 1;140(7):1609-1619. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30543. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Int J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 27914100 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1) protects liver damage by suppressing IFN-γ expression in T cells in infants and neonatal mice.BMC Pediatr. 2021 Jul 16;21(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s12887-021-02794-x. BMC Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34271894 Free PMC article.
-
The Paradoxical Roles of Inflammation during PD-1 Blockade in Cancer.Trends Immunol. 2020 Nov;41(11):982-993. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.09.003. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Trends Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33036910 Review.
Cited by
-
Hip Fracture Leads to Transitory Immune Imprint in Older Patients.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 18;11:571759. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.571759. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33072114 Free PMC article.
-
Potential diagnostic value of PD-1 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of postmenopausal osteoporosis patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jun;34(6):e23223. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23223. Epub 2020 Feb 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32065479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li S. G., Sun T. S., Liu Z., Ren J. X., Liu B., Gao Y. Factors influencing postoperative mortality one year after surgery for hip fracture in Chinese elderly population. Chinese Medical Journal. 2013;126(14):2715–2719. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

