Lobectomy on ECMO as a Life-Saving Procedure following Necrotizing Pneumonia in a Toddler: A Case Study
- PMID: 31073496
- PMCID: PMC6506680
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1636507
Lobectomy on ECMO as a Life-Saving Procedure following Necrotizing Pneumonia in a Toddler: A Case Study
Abstract
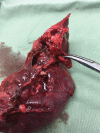
Necrotizing pneumonia is a severe form of pneumonia that is mainly treated with conservative treatment, including antibiotics. We report a unique case of necrotizing pneumonia due to group A streptococcus infection in an 18-month-old boy who required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support. Following surgical lobectomy, the child was weaned off ECMO and recovered uneventfully.
Keywords: ECMO; lobectomy; necrotizing pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Erlichman I, Breuer O, Shoseyov D et al. Complicated community acquired pneumonia in childhood: different types, clinical course, and outcome. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2017;52(02):247–254. - PubMed
-
- Lai J Y, Yang W, Ming Y C. Surgical management of complicated necrotizing pneumonia in children. Pediatr Neonatol. 2017;58(04):321–327. - PubMed
-
- Thiagarajan R R, Barbaro R P, Rycus P T et al. Extracorporeal Life Support Organization Registry International Report 2016. ASAIO J. 2017;63(01):60–67. - PubMed
-
- Stroud M H, Okhuysen-Cawley R, Jaquiss R, Berlinski A, Fiser R T. Successful use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in severe necrotizing pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2007;8(03):282–287. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources