Critical role for Piccolo in synaptic vesicle retrieval
- PMID: 31074746
- PMCID: PMC6541439
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.46629
Critical role for Piccolo in synaptic vesicle retrieval
Abstract
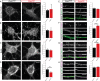
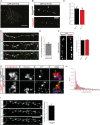
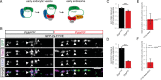
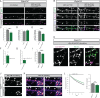
Loss of function of the active zone protein Piccolo has recently been linked to a disease, Pontocerebellar Hypoplasia type 3, which causes brain atrophy. Here, we address how Piccolo inactivation in rat neurons adversely affects synaptic function and thus may contribute to neuronal loss. Our analysis shows that Piccolo is critical for the recycling and maintenance of synaptic vesicles. We find that boutons lacking Piccolo have deficits in the Rab5/EEA1 dependent formation of early endosomes and thus the recycling of SVs. Mechanistically, impaired Rab5 function was caused by reduced synaptic recruitment of Pra1, known to interact selectively with the zinc finger domains of Piccolo. Importantly, over-expression of GTPase deficient Rab5 or the Znf1 domain of Piccolo restores the size and recycling of SV pools. These data provide a molecular link between the active zone and endosome sorting at synapses providing hints to how Piccolo contributes to developmental and psychiatric disorders.
Keywords: Piccolo; Rab5; early endosomes; neuroscience; rat; recycling; synaptic vesicles.
© 2019, Ackermann et al.
Conflict of interest statement
FA, KS, CB, ZI, FH, CR, CG No competing interests declared
Figures

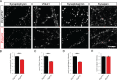
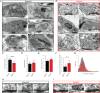
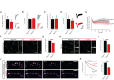
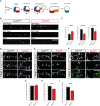

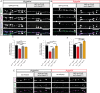
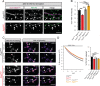
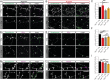
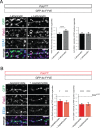



References
-
- Ahmed MY, Chioza BA, Rajab A, Schmitz-Abe K, Al-Khayat A, Al-Turki S, Baple EL, Patton MA, Al-Memar AY, Hurles ME, Partlow JN, Hill RS, Evrony GD, Servattalab S, Markianos K, Walsh CA, Crosby AH, Mochida GH. Loss of PCLO function underlies pontocerebellar hypoplasia type III. Neurology. 2015;84:1745–1750. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001523. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arancillo M, Min SW, Gerber S, Münster-Wandowski A, Wu YJ, Herman M, Trimbuch T, Rah JC, Ahnert-Hilger G, Riedel D, Südhof TC, Rosenmund C. Titration of Syntaxin1 in mammalian synapses reveals multiple roles in Vesicle Docking, priming, and release probability. Journal of Neuroscience. 2013;33:16698–16714. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0187-13.2013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- SFB958/Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft/International
- ERC Advanced/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- Early carrier development grant/Norwegian Cancer Society/International
- R01HD053889/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R24RR03232601/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R24OD011108/NIH Office of the Director/International
- ERC Advanced ERC-2011-AdG 294742/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- NGFN-2 NGFNplus - ENGINE/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung/International
- R01HD061575/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- early carrier development grant/Norwegian Cancer Society/International
- R01HD053889 and R01HD061575/National Institute of Health/International
- R24OD011108/The Office of the Director/International
- ERC Advanced,ERC-2011-AdG 294742/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- NGFN-2,NGFNplus - ENGINE/Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

