Gamma Entrainment Binds Higher-Order Brain Regions and Offers Neuroprotection
- PMID: 31076275
- PMCID: PMC6697125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.04.011
Gamma Entrainment Binds Higher-Order Brain Regions and Offers Neuroprotection
Abstract
Neuronal and synaptic loss is characteristic in many neurodegenerative diseases, such as frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer's disease. Recently, we showed that inducing gamma oscillations with visual stimulation (gamma entrainment using sensory stimuli, or GENUS) reduced amyloid plaques and phosphorylated tau in multiple mouse models. Whether GENUS can affect neurodegeneration or cognitive performance remains unknown. Here, we demonstrate that GENUS can entrain gamma oscillations in the visual cortex, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex in Tau P301S and CK-p25 mouse models of neurodegeneration. Tau P301S and CK-p25 mice subjected to chronic, daily GENUS from the early stages of neurodegeneration showed a preservation of neuronal and synaptic density across multiple brain areas and modified cognitive performance. Our transcriptomic and phosphoproteomic data suggest that chronic GENUS shifts neurons to a less degenerative state, improving synaptic function, enhancing neuroprotective factors, and reducing DNA damage in neurons while also reducing inflammatory response in microglia.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTEREST
L.-H.T. and E.S.B are scientific co-founders and serve on the scientific advisory board of Cognito Therapeutics.
Figures


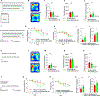
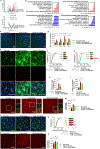
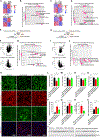
Comment in
-
Leaving the Lights on Using Gamma Entrainment to Protect against Neurodegeneration.Neuron. 2019 Jun 5;102(5):901-902. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.05.020. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 31170394
References
-
- Balschun D, Moechars D, Callaerts-Vegh Z, Vermaercke B, Van Acker N, Andries L, and D’hooge R (2009). Vesicular glutamate transporter VGLUT1 has a role in hippocampal long-term potentiation and spatial reversal learning. Cerebral Cortex 20, 684–693. - PubMed
-
- Benveniste EN, Nguyen VT, Wesemann DR. (2004) Molecular regulation of CD40 gene expression in macrophages and microglia. Brain Behav Immun 18(1):7–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

