Inflammasome Activation Triggers Blood Clotting and Host Death through Pyroptosis
- PMID: 31076358
- PMCID: PMC6791531
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.04.003
Inflammasome Activation Triggers Blood Clotting and Host Death through Pyroptosis
Abstract
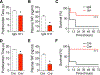
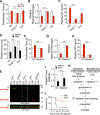
Inflammasome activation and subsequent pyroptosis are critical defense mechanisms against microbes. However, overactivation of inflammasome leads to death of the host. Although recent studies have uncovered the mechanism of pyroptosis following inflammasome activation, how pyroptotic cell death drives pathogenesis, eventually leading to death of the host, is unknown. Here, we identified inflammasome activation as a trigger for blood clotting through pyroptosis. We have shown that canonical inflammasome activation by the conserved type III secretion system (T3SS) rod proteins from Gram-negative bacteria or noncanonical inflammasome activation by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced systemic blood clotting and massive thrombosis in tissues. Following inflammasome activation, pyroptotic macrophages released tissue factor (TF), an essential initiator of coagulation cascades. Genetic or pharmacological inhibition of TF abolishes inflammasome-mediated blood clotting and protects against death. Our data reveal that blood clotting is the major cause of host death following inflammasome activation and demonstrate that inflammasome bridges inflammation with thrombosis.
Keywords: DIC; GSDMD; LPS; caspase; coagulation; inflammasome; macrophage; pyroptosis; sepsis; tissue factor.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
D.K. is an employee of Genentech Inc. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


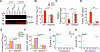

Comment in
-
Death Is Coming and the Clot Thickens, as Pyroptosis Feeds the Fire.Immunity. 2019 Jun 18;50(6):1339-1341. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.05.015. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 31216455
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 GM121796/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL123927/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI103717/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016086/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI137020/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142640/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM132443/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI142063/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM085231/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM127211/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103527/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL145117/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

