A Precision B Cell-Targeted Therapeutic Approach to Autoimmunity Caused by Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Pathway Dysregulation
- PMID: 31076529
- PMCID: PMC6548689
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801394
A Precision B Cell-Targeted Therapeutic Approach to Autoimmunity Caused by Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Pathway Dysregulation
Abstract
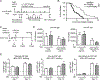
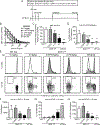
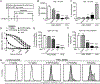
The inositol lipid phosphatases PTEN and SHIP-1 play a crucial role in maintaining B cell anergy and are reduced in expression in B cells from systemic lupus erythematosus and type 1 diabetes patients, consequent to aberrant regulation by miRNA-7 and 155. With an eye toward eventual use in precision medicine therapeutic approaches in autoimmunity, we explored the ability of p110δ inhibition to compensate for PI3K pathway dysregulation in mouse models of autoimmunity. Low dosages of the p110δ inhibitor idelalisib, which spare the ability to mount an immune response to exogenous immunogens, are able to block the development of autoimmunity driven by compromised PI3K pathway regulation resultant from acutely induced B cell-targeted haploinsufficiency of PTEN and SHIP-1. These conditions do not block autoimmunity driven by B cell loss of the regulatory tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. Finally, we show that B cells in NOD mice express reduced PTEN, and low-dosage p110δ inhibitor therapy blocks disease progression in this model of type 1 diabetes. These studies may aid in the development of precision treatments that act by enforcing PI3K pathway regulation in patients carrying specific risk alleles.
Copyright © 2019 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures

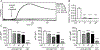
References
-
- Halverson R, Torres RM, and Pelanda R. 2004. Receptor editing is the main mechanism of B cell tolerance toward membrane antigens. Nat Immunol 5: 645–650. - PubMed
-
- Nemazee DA, and Burki K. 1989. Clonal deletion of B lymphocytes in a transgenic mouse bearing anti-MHC class I antibody genes. Nature 337: 562–566. - PubMed
-
- Cyster JG, Hartley SB, and Goodnow CC. 1994. Competition for follicular niches excludes self-reactive cells from the recirculating B-cell repertoire. Nature 371: 389–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

