Heterozygous Variants in KMT2E Cause a Spectrum of Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Epilepsy
- PMID: 31079897
- PMCID: PMC6556837
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.03.021
Heterozygous Variants in KMT2E Cause a Spectrum of Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Epilepsy
Abstract
We delineate a KMT2E-related neurodevelopmental disorder on the basis of 38 individuals in 36 families. This study includes 31 distinct heterozygous variants in KMT2E (28 ascertained from Matchmaker Exchange and three previously reported), and four individuals with chromosome 7q22.2-22.23 microdeletions encompassing KMT2E (one previously reported). Almost all variants occurred de novo, and most were truncating. Most affected individuals with protein-truncating variants presented with mild intellectual disability. One-quarter of individuals met criteria for autism. Additional common features include macrocephaly, hypotonia, functional gastrointestinal abnormalities, and a subtle facial gestalt. Epilepsy was present in about one-fifth of individuals with truncating variants and was responsive to treatment with anti-epileptic medications in almost all. More than 70% of the individuals were male, and expressivity was variable by sex; epilepsy was more common in females and autism more common in males. The four individuals with microdeletions encompassing KMT2E generally presented similarly to those with truncating variants, but the degree of developmental delay was greater. The group of four individuals with missense variants in KMT2E presented with the most severe developmental delays. Epilepsy was present in all individuals with missense variants, often manifesting as treatment-resistant infantile epileptic encephalopathy. Microcephaly was also common in this group. Haploinsufficiency versus gain-of-function or dominant-negative effects specific to these missense variants in KMT2E might explain this divergence in phenotype, but requires independent validation. Disruptive variants in KMT2E are an under-recognized cause of neurodevelopmental abnormalities.
Keywords: H3K4 methylation; KMT2E; autism; epilepsy; epileptic encephalopathy; global developmental delay; intellectual disability; neurodevelopmental disorder.
Copyright © 2019 American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
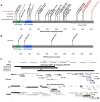

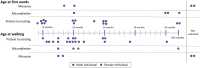

References
-
- Shen E., Shulha H., Weng Z., Akbarian S. Regulation of histone H3K4 methylation in brain development and disease. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014;369:369. - PMC - PubMed
- Shen, E., Shulha, H., Weng, Z., and Akbarian, S. (2014). Regulation of histone H3K4 methylation in brain development and disease. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 369, 369. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jones W.D., Dafou D., McEntagart M., Woollard W.J., Elmslie F.V., Holder-Espinasse M., Irving M., Saggar A.K., Smithson S., Trembath R.C. De novo mutations in MLL cause Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012;91:358–364. - PMC - PubMed
- Jones, W.D., Dafou, D., McEntagart, M., Woollard, W.J., Elmslie, F.V., Holder-Espinasse, M., Irving, M., Saggar, A.K., Smithson, S., Trembath, R.C., et al. (2012). De novo mutations in MLL cause Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 91, 358-364. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zech M., Boesch S., Maier E.M., Borggraefe I., Vill K., Laccone F., Pilshofer V., Ceballos-Baumann A., Alhaddad B., Berutti R. Haploinsufficiency of KMT2B, encoding the lysine-specific histone methyltransferase 2B, results in early-onset generalized dystonia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016;99:1377–1387. - PMC - PubMed
- Zech, M., Boesch, S., Maier, E.M., Borggraefe, I., Vill, K., Laccone, F., Pilshofer, V., Ceballos-Baumann, A., Alhaddad, B., Berutti, R., et al. (2016). Haploinsufficiency of KMT2B, encoding the lysine-specific histone methyltransferase 2B, results in early-onset generalized dystonia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 99, 1377-1387. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koemans T.S., Kleefstra T., Chubak M.C., Stone M.H., Reijnders M.R.F., de Munnik S., Willemsen M.H., Fenckova M., Stumpel C.T.R.M., Bok L.A. Functional convergence of histone methyltransferases EHMT1 and KMT2C involved in intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder. PLoS Genet. 2017;13:e1006864. - PMC - PubMed
- Koemans, T.S., Kleefstra, T., Chubak, M.C., Stone, M.H., Reijnders, M.R.F., de Munnik, S., Willemsen, M.H., Fenckova, M., Stumpel, C.T.R.M., Bok, L.A., et al. (2017). Functional convergence of histone methyltransferases EHMT1 and KMT2C involved in intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder. PLoS Genet. 13, e1006864. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van Laarhoven P.M., Neitzel L.R., Quintana A.M., Geiger E.A., Zackai E.H., Clouthier D.E., Artinger K.B., Ming J.E., Shaikh T.H. Kabuki syndrome genes KMT2D and KDM6A: functional analyses demonstrate critical roles in craniofacial, heart and brain development. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015;24:4443–4453. - PMC - PubMed
- Van Laarhoven, P.M., Neitzel, L.R., Quintana, A.M., Geiger, E.A., Zackai, E.H., Clouthier, D.E., Artinger, K.B., Ming, J.E., and Shaikh, T.H. (2015). Kabuki syndrome genes KMT2D and KDM6A: functional analyses demonstrate critical roles in craniofacial, heart and brain development. Hum. Mol. Genet. 24, 4443-4453. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

